A rise in imports from Australia drove Japanese thermal coal receipts sharply higher on the year in August, following strong generation from fossil fuels in July.
But the demand outlook for the rest of the year looks soft, amid continuing coronavirus restrictions, recovering nuclear availability and with oil-linked LNG expected to become increasingly competitive on cost with spot coal this winter.
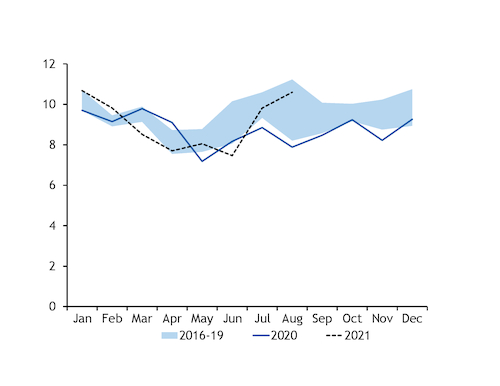
Japanese thermal coal imports rose by 2.7mn t on the year to 10.6mn t in August, according to provisional finance ministry data released today. This was the strongest annual growth for at least 11 years following an unusually low take last year, and the biggest August receipt since 2018.
The provisional figures do not include imports of low-ash bituminous coal of mostly Indonesian origin, which averaged around 1.7mn t/month in January-July.
Year-to-date imports excluding low-ash bituminous coal stood at 72.7mn t, compared with 70mn t last year and a 2017-19 average of 75.2mn t for the first eight months of the year.
The increase in August followed a strong month for fossil fuel-based generation in July, which rose by 3.7TWh on the year to 56.3TWh.
Japanese utilities may also have upped their receipts to tackle low inventory levels — aggregate power-sector stocks as of the end of May were 1.4mn t down on the year at 8.5mn t, although this was only 200,000t lower than the three-year seasonal average.
But seaborne demand looks set to wane in the remainder of the year, as thermal generation probably fell sharply in August on lower power demand and recovering nuclear availability, and with extended coronavirus restrictions painting a weak outlook for power demand in the near term.
Nuclear availability is scheduled to average 8.6GW over September-December, meaning output will likely grow on the year by 3.8-4.7TWh each month. This would be more than enough to offset a recovery in overall power demand to the four-year seasonal average, creating further downside potential for flexible thermal generation that would need to give way to balance higher nuclear output.
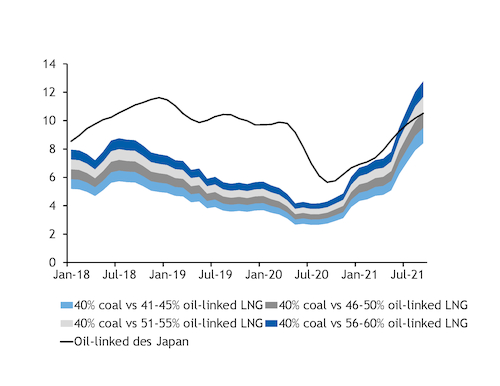
And coal may come under additional pressure as oil-linked LNG prices have become increasingly competitive with spot thermal coal prices. This should create a strong incentive for utilities to maximise their offtake from term LNG agreements, minimise their draw on term coal deals and limit spot purchases, although optimising in this way this will depend on the remaining flexibility within buyers' LNG term contracts.
The value of Japanese LNG imports remains highly correlated with oil-linked prices, since this is the mechanism accounting for the majority of purchases. Fourth-quarter oil-linked LNG prices are expected to average around $10.65/mn Btu, according to Argus' prices.
This is below implied coal-switching prices based on Japan-delivered NAR 6,000 kcal/kg Australian coal prices and factoring in coal and LNG consumption taxes. Oil-linked LNG used in 55pc efficient gas-fired plants would be competitive with spot coal burned in 40pc efficient coal-fired plants at around $12/mn Btu or lower, according to Argus analysis.
In January-May — the latest period for which data are available — Japanese gas-fired generation rose by 4pc on the year to 141.5TWh, while coal-fired generation fell by 2pc to 111.7TWh.
Cumulative 2021 LNG imports have also outpaced seaborne coal receipts, rising by 6.7pc to 51.4mn t of LNG, compared with a 3.9pc increase to 72.7mn t for thermal coal in January-August.
Australia leads rise in imports
Australia accounted for nearly all of the annual growth in Japanese imports in August, with receipts up by as much as 2.6mn t to 7.8mn t.
This total may include small volumes of South African, Colombian or Canadian coal, which are not broken out in the provisional data.
Imports from the US rose by 412,000t to a possible record 560,000t while receipts from Russia fell by 160,000t to 1.3mn t. Imports from Indonesia — excluding low-ash bituminous coal — were stable at around 900,000t.