Uptake of coal deliveries from the Amsterdam-Rotterdam-Antwerp (ARA) trading hub to south Germany continued to be lacklustre this week as the call on German coal-fired generation remains limited with the exception of sporadic increases in power sector coal burn.
This suggests that German coal plant operators might be unable to take deliveries at relaxed barge rates because their stocks are amply filled, which in turn exposes them to the risk of another dry summer period.
Water levels on the Rhine have been in range of 155-185cm at the Kaub measuring point since the end of April, data from water and shipping agency WSV show.
Kaub is the narrowest point barges travelling to south Germany have to pass. Plant operators typically pay a surcharge on top of the standard barge rate of €5/t from ARA to the south German city of Mannheim once Kaub levels move below 180cm, while levels well above that threshold can lower rates. With Rhine levels at Kaub neither significantly below nor above 180cm since the end of April, barge rates have been fairly stable.
Barge rates for that journey have not exceeded €8/t since the end of February. And coal deliveries booked from ARA to Mannheim cost around €5.70/t yesterday, when WSV put the Kaub level at 166cm, one barge operator said.
But demand for booking large vessels which can carry up to 4,500-5,000/t from ARA to south Germany continues to be lower than usual, the barge operator said. Typically, barge rates around the standard tariff provide an incentive to replenish stocks at plant sites to ease the need to take deliveries at times of lower water levels and subsequently higher transport costs.
But while German power sector coal burn has recovered this week to move well above daily average output in March and April, it remains well below the five-year average for May. Coal-fired power generation reached the lowest level for any month at least since the start of this decade in March, at a daily average of 4.8GW, as record-high wind power generation increased the share of renewable energy generation in the German electricity generation mix to a new all-time high, data from German research institute Fraunhofer Ise show. In April, coal-fired generation increased just slightly to 5.3GW, based on the Fraunhofer Ise data.
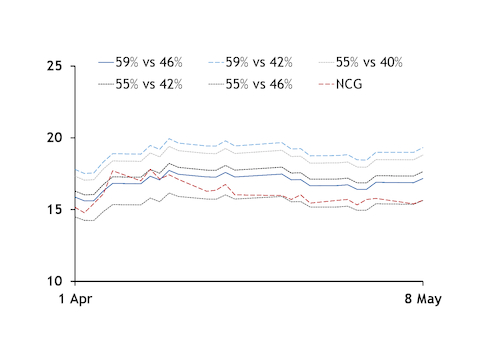
Coal vs gas
With wind power generation trailing behind output in recent weeks, the share of combined renewable energy generation — which includes output from hydro, biomass, wind and solar photovoltaic capacity — in the German electricity generation mix fell to an average of 46pc so far this week, compared with 54pc last week and 49.4pc across April, according to the Fraunhofer Ise data.
Based on price signals alone, the German short-term market has been deeply in coal-to-gas fuel switch territory since mid-April. Working day-ahead clean spark spreads for gas plants with efficiency of 55pc or higher have been consistently above clean dark spreads for coal-fired plants with efficiency of 42pc or lower. But a number of efficient gas-fired units have been off line for maintenance since the end of April.
This allowed coal-fired power generation to rise to a daily average of 8.3GW on 6-8 May from 4.9GW the previous week, while gas-fired generation rose to just 4.2GW on average so far this week from 3.1GW in week 18, which covered 29 April to 5 May, Fraunhofer data show. But with the exception of last year, German coal-fired power generation in May was higher and held above 10GW in most years, while gas-fired power generation hovered below 4GW in May 2013-18 with the exception of May 2017.
And the rise in coal-fired power generation early this week has so far failed to result in rising demand for taking coal from ARA to German plant sites.
Implications for H2
This suggests that coal stocks at power plants continue to be amply filled, with the result of German utilities being unable to benefit from barge rates hovering around the standard tariff.
In the third quarter of last year, barge rates from ARA to Mannheim rose to a high of €21/t in September after water levels at Kaub fell to as low as 60cm.
At the time, gas-fired generation had been largely non-competitive with coal burn because of strong injection demand into storage as the latter had been depleted following the 2017-18 winter season. This meant that coal burn was deeply embedded in the German generation mix in the third quarter of last year even as barge rates rose, with German forward contracts and the day-ahead market delivering over the period finding support from strong demand for power sector coal burn and the need for gas burn to meet domestic and cross-border demand.
At prevailing prices, the situation is reversed this summer. The third-quarter NCG gas hub contract yesterday closed comfortably below the level at which a 55pc-efficent gas plant would be competitive with a 42pc-efficient coal plant, and just slightly above the level at which a 55pc-efficient gas-fired unit would be able to compete with a 46pc-efficient coal-fired plant. The latter is the highest efficiency for hard coal power plants in Germany. This pushes older German coal-fired to the margin of the expected German merit order in the third quarter. Low river levels and subsequent higher barge rates would then have less of an impact on the German wholesale power price should coal-to-gas fuel switching remain firm in delivery in the third quarter, as low load factors for coal plants would translate into continued limited demand to replenish stocks.
But a repeat of a sustained period of dry weather conditions could have a more material impact on wholesale power prices in the fourth quarter when coal-to-gas fuel switch potential eases. In the fourth quarter of last year, barge rates for delivery from ARA to Mannheim hit a high of €41/t, which added €14.49/MWh to the operational costs of a 40pc-efficient coal plant. The standard tariff at €5/t adds just €1.56/MWh to the operational costs of such units.