US LNG deliveries to Europe are poised to slow down from around the second week of February after US firms redirected feedgas towards higher-priced domestic markets.
A winter storm has hit the southeast of the US, leading to soaring local gas prices and prompting offtakers from LNG facilities with the flexibility to do so to redirect their feedgas towards the domestic market.
Spot feedgas costs at six of the eight LNG export terminals in the country spiked on Monday. Weighted-average feedgas costs to the 4mn t/yr Elba Island and the 5.75mn t/yr Cove Point terminals hit all-time highs of $96.36/mn Btu and $93.76/mn Btu, respectively. These prices were at significant premiums to delivered LNG prices for cargoes arriving in northwest Europe in the second half of February, which were $13/mn Btu that day.
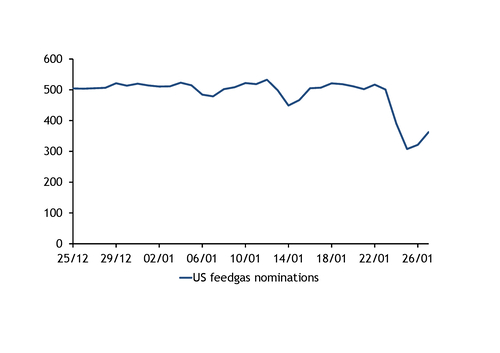
Feedgas nominations from interstate pipelines fell to a one-year low of 308mn m³ on 25 January, down from 390mn m³ a day earlier and the 30-day average of 506mn m³/d before the storm began affecting flows on 23 January, pipeline data show. Nominated flows ticked up to 321mn m³ on Monday before stepping higher to 363mn m³ today. The reduction in feedgas nominations on 24-27 January is equivalent to about seven fewer LNG cargoes.
Abnormally cold weather is forecast to persist through the end of the week, which may continue to reduce feedgas to US terminals. Gulf coast terminals need several days to return to normal operations, and persistent cold along the Atlantic coast may encourage traders to keep more gas in domestic markets.
Reduced LNG loadings could weigh on deliveries to Europe from 6 February onwards, considering it takes 13 days to ship a cargo from Texas' 17.3mn t/yr Freeport LNG to the UK's Milford Haven, with another shipping day added for deliveries to the Gate terminal in the Netherlands.
Less US LNG arriving in Europe is poised to further tighten Europe's delicate supply balance for the remainder of the winter. Slower sendout may push firms to draw more heavily from storage at a time when stocks are already unusually low. Underground sites across the EU were 44.4pc full and held 507TWh as of Monday morning, which is 130TWh less than the five-year average for that date.
Additionally, the reduction in US LNG imports could slow down sendout at the same time colder weather is set to hit some parts of northwest Europe. Overnight lows in the UK and Amsterdam are forecast to dip 1-2°C below the seasonal norm on 9-15 February, from holding 0.5-1.5°C above average earlier that month.
European gas prices have opened up a large premium to LNG prices for delivery to northeast Asia, leading firms to direct some cargoes from further into the Pacific towards Europe instead of Asia despite the much longer shipping journey. But the replacement cargoes from outside the Atlantic basin are unlikely to get to Europe in time for February. Reduced US LNG supply has led to fewer offers for deliveries into Europe for the second half of February and kept delivered LNG prices' discounts to the TTF tighter for the second half of February than for March, where stronger offers have pushed des-TTF differentials to two-year highs.
The 174,000m³ Qingcheng altered its course towards northeast Asia in the mid-Pacific after loading at the 14mn t/yr LNG Canada facility and appeared as of this afternoon to be heading to Europe through the Panama Canal, an uncommon LNG shipping route. Meanwhile, the 170,000m³ Methane Julia Louise appears to be bound for Europe around the Cape of Good Hope with an Australian cargo on board.