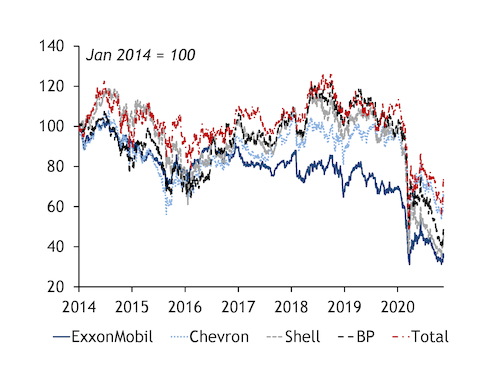
ExxonMobil has arguably been playing by the "go big or go home" mantra for many years now. This may be the year it has to do the latter.
It was once seen as the gold standard among US corporations and global oil firms, building and operating massive projects from Alberta to Sakhalin, Guyana to the Kara Sea. But the 2020 oil market collapse has hit ExxonMobil particularly hard. It suffered its first consecutive quarterly losses in decades, will not be upping its dividend for the first year ever, and has made deep and wide job and operational cuts across the globe — the kind of cuts competitors regularly made but it had long vowed to avoid. To add insult to injury, ExxonMobil was removed from the Dow Jones Industrials index this year, ending 92 years on the blue-chip list. Rival Chevron, which last month overtook ExxonMobil's market capitalisation — of around $150bn — for the first time, remains the lone oil firm on the list.
The second oil price slump in five years has flagged up the danger of ExxonMobil's counter-cyclical capital expenditure (capex) plans, which it is now reining in sharply to defend dividends. And lower oil and gas prices have left it facing the prospect of massive impairments on US gas assets. Like many international energy giants, it mistimed the shale revolution, selling much of its US onshore position early in the 2000s only to try to buy back in through the $41bn XTO purchase in 2009. The company now says it may finally take the plunge that many others have made before — taking a $25bn-$30bn write-down on its XTO shale assets, and writing down some of its Canadian Kearl oil sands investment.
While its peers have all constrained their capex since 2016, ExxonMobil was set to increase capex to as much as $35bn next year until this year's price crash. Its outlook now is for $16bn-19bn in 2021. But the aggressive dividend growth that started in 2012 has now reached $3.7bn per quarter. ExxonMobil generated $4.4bn in cash from operations in the third quarter, resulting in a net debt increase of $3bn — a pace that in theory could make it unable to pay the dividend by late next year.
Traditionally, the firm has had a steady stream of asset sales to draw on — so steady it did not even break them out as special items the same way competitors might. This year, with the dividend stressed and few buyers, it may need to turn to selling its stake in joint ventures and partnerships around the globe.
ExxonMobil laid out a strategy in its most recent earnings that has at its heart a very un-ExxonMobil notion — hope. Hope that the global recession has bottomed out, and that demand and prices will be on the upswing. Hope that a resumption of travel and commerce will make 2021 a good year for refiners and petrochemicals, in which the firm has a strong position. And hope that all of the deep cuts its peers have made this year will mean an underinvestment in supply in just a few years' time, setting the stage for the next boom cycle when demand outpaces supply.
Risky business
Sticking to the course means maintaining the dividend — even though it cannot afford it for long. But with nearly 48pc of ExxonMobil's shares owned by retail investors, cutting the dividend carries more weight than simple maths.
The balancing act ExxonMobil is trying to pull off is risky, but it has few choices. Its big projects, such as its operating stake in offshore Guyana oil production, will continue to throw out cash for years to come. A reinvention for investors with an eye toward the energy transition is unlikely — ExxonMobil's name is more likely to be tied to climate denial than renewables by investors, despite being an early proponent of a carbon tax. And a share price that has fallen further from the heights of 2014 than that of any of its peers raises an inevitable question — are ExxonMobil's best days already far behind it?