Continued low demand from downstream industries, a fall in feedstock costs and lower bid prices from key consumers have weighed on the tungsten market since the start of November, after prices rose to three-year highs in late October.
Prices for 88.5pc grade ammonium paratungstate (APT) were last assessed at 164,000-166,000 yuan/t ($290-294/t) on 18 November, down by Yn3,000/t from 16 November and by Yn5,000/t from a week earlier.
The range hit a more than three-year high at Yn172,000-175,000/t on 21 October, driven by a sharp rise in ingredient costs for caustic soda, sulphuric acid and ammonium sulfide as well as power supply curbs in the main production hub of Ganzhou city in Jiangxi province. The range then held at the high level in the final week of October and started to soften from 2 November.
Buying interest from key consumption fields including automotive, construction, aerospace and other industrial sectors is less robust than the first three quarters, according to market participants.
Domestic sales of excavators totalled 18,964 in October, down by 31pc on the year, although higher sales in the first three quarters pushed January-October sales up by 13pc on the year. China invested around Yn8.85bn in its real estate sector during January-August, up by 4.6pc on the year, according to data from the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS)
China's January-October investment in the real estate sector rose by 7.2pc on year and by 14pc from the same period in 2019. October investment fell by 5.4pc on the year, a second consecutive monthly decline and the only declines since the outbreak of the Covid-19, according to NBS data.
China's vehicle output fell by 8.8pc from a year earlier to 23.3mn units in October, with sales decreasing by 9.4pc to 2.33mn units, according to data from the China Automotive Manufacturers Association. Automotive output in the whole of 2022 is forecast to fall from previously-expected growth of 4pc because of continued semiconductor shortages.
Processing costs from concentrate to APT moved up to around Yn16,000/t in mid-October when prices for processing ingredients caustic soda and sulphuric acid kept rising because of energy consumption restrictions. The processing cost in November fell back to Yn12,000-13,000/t following lower prices for caustic soda and ammonium sulfide. Lower feedstock costs have created room for APT producers to cut offers to attract sales in view of limited buying interest from downstream consumers.
Key consumers' lower bid prices in November also dented market confidence and prompted traders to destock at lower prices to take profit before further downside potential. Zhangyuan lowered its first-half November bid price for 88.5pc grade APT by 1,500 yuan/t to Yn170,500/t from Yn172,000/t in the second half of October. Xianglu's bid price for APT fell by 4,200 yuan/t to Yn170,500/t from the second-half October price of Yn174,700/t. Xiamen Tungsten cut its first-half November bid price for APT by Yn1,000/t to Yn171,000/t and further reduced it this week by Yn5,000/t for the second half. Xiamen Tungsten's lower bids raised market concerns of a potential downside and prompted downstream consumers to scale back purchases and adopt a wait-and-see approach. A few sellers cut spot offers to Yn164,000/t this week, Yn2,000/t lower than Xiamen Tungsten's bid prices, in an effort to secure deals before the year-end.
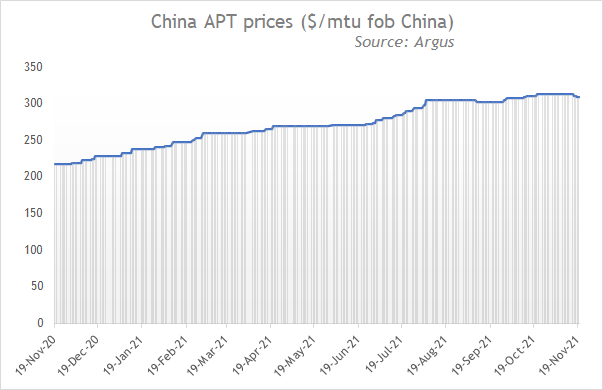
Export prices for APT were assessed at $306-311/mtu on 18 November, down by $4/mtu from a week earlier, which is slower than the fall in domestic prices, as key exporters were unwilling to cut offers considering continued delayed shipping periods, tight spot availability outside of China and firm prices in the European and US markets. Argus assessed prices for APT stable at $320-325/mtu in Rotterdam from 21 October to today.