Some eastern US utilities are considering taking more Powder River basin (PRB) coal because of limited supply and higher prices for Appalachian and Illinois basin coal.
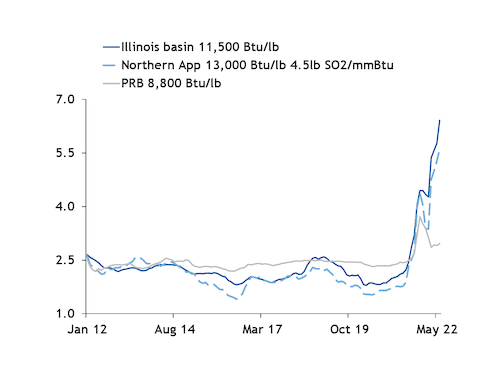
Premiums for Illinois basin and Appalachian coal over PRB coal are at historic levels, according to Argus data going back to September 2009. That reflects near record high prices for higher heat content coals. PRB prices are also elevated but have retreated from records reached in the autumn of 2021 as supply has loosened.
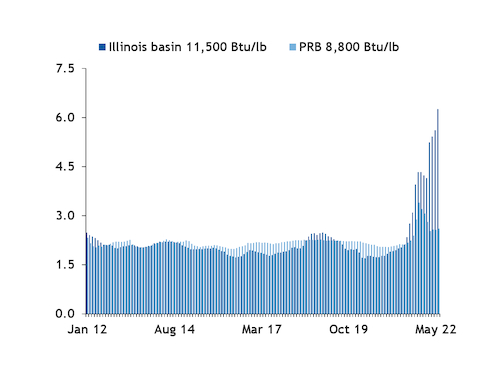
Around St. Louis, Missouri, and the central portion of the Midcontinent Independent System Operator, for example, the delivered cost of Illinois basin 11,500 Btu/lb 5lb SO2/mmBtu coal within the Illinois basin averaged $5.615/mmBtu in May, more than double the $2.562/mmBtu average for PRB 8,800 Btu/lb coal delivered to St. Louis during the same period. And delivered costs for Pittsburgh Seam 13,000 Btu/lb 4.5lb SO2/mmBtu coal and Illinois basin coal to southwest Ohio — in the PJM Interconnection — averaged an estimated $5.231/mmBtu and $5.763/mmBtu, respectively, while PRB coal was $2.910/mmBtu.
A year earlier, PRB coal to St. Louis and southwest Ohio was more expensive than Illinois basin and Northern Appalachian coal.
Eastern US coal producers are expecting prices to remain elevated as long as international coal prices remain higher. They also do not expect any significant increase in Appalachian and Illinois basin coal production.
This has led some buyers to examine whether they can take more PRB coal.
"Price volatility in the various coal production regions, in general, could drive modest changes in the supply mix for some utilities," said Northern Indiana Public Service Company, which took rail coal from Wyoming, Illinois and northern West Virginia last year. "However, there are serious rail transportation constraints that are affecting almost all commodities shipped by rail."
In general, basin-related fuel switching would take some time because of "location and delivery issues, boiler compatibility considerations, stockpile/blending constraints and even air emission permit concerns," the US Energy Information Administration's (EIA) electricity team said.
Power plants in the Midwest burning Illinois basin coal are the primary candidates for purchasing more PRB coal, mostly because of proximity, according to EIA. Plants further east that could get PRB coal shipped by railroad to terminals on the Ohio or Mississippi rivers, and then delivered by barge, could be candidates as well.
"But we need to know the PRB supply is going to be there," one buyer said.
EIA expects western US coal production to rise in 2022 and again in 2023 to 354mn st, up from 329mn st last year, according to the agency's latest Short-Term Energy Outlook. Output from the Appalachias, which totaled 156mn st in 2021, is projected to inch up to 158mn st this year but dip in 2023 to 147mn st. In the interior US, which includes the Illinois basin, production is forecast to fall to 87mn st next year from roughly 93mn st in 2021 and 2022.
Peabody Energy, the top PRB coal seller, said in April it is hiring workers and making investments in its PRB operations, and that output from that region and the company's other US thermal coal business will ramp up through the third quarter.
Arch Resources is also targeting higher coal sales this year compared to 2021, but it does not expect to have significant gains in thermal coal output. Some Illinois basin and Appalachian coal producers have made similar comments on production.
But fuel switching is more complicated than whether coal from a particular region is available.
"With PRB, you need to burn a lot more of the coal, so is the plant capable of processing all of that coal? It can possibly present operational challenges," the buyer said.
Some utilities could choose to run plants that already take PRB coal at greater rates than plants taking eastern coal. And a few other eastern utilities said they have the flexibility to take more PRB coal but that transportation would be the biggest obstacle.
"Most utilities are struggling to receive the commitments they have for the plants that normally consume PRB coal, so adding to that taxed rail system would only make the issue worse for western plants," another buyer said.
Some western US coal producers also are dubious about railroads' abilities to increase shipments. Western US railroads were slower last month to haul loaded coal cars despite utility calls for more shipments.
In the four weeks through 27 May, western railroad BNSF averaged 167 coal cars/week that were loaded but had not moved in more than two days, more than double the amount from a year earlier, Surface Transportation Board data show. The number of loaded coal cars Union Pacific had not moved in more than two days jumped to 498 cars/week from 58 cars/week a year earlier.
Some utilities said they do not expect to make significant changes in the mix of coal types they take. We Energies, whose Elm Road Generating Station in Wisconsin took Pennsylvania and Wyoming coal last year, said it does not anticipate any significant changes in its coal mix.
Louisville Gas & Electric (LG&E) and Kentucky Utilities (KU) made similar comments. "Despite the current climate," the utilities predominant use of Illinois basin coal has not changed, "thanks in large part to our procurement approach."
Having a portfolio of long-term coal supply contracts, which can last up to six years and are "still priced favorably," helps shield LG&E and KU from volatile coal prices, the utilities said.
Southern Company subsidiary Georgia Power declined to discuss future coal purchases but said it has options for longer-term coal mix adjustments if fundamental market changes occur.