Weak coal burn and ample stockpiles cut thermal coal imports to the EU by the widest margin so far this year and for the fifth consecutive month in June.
Net receipts from non-EU members totalled 6.18mn t in June, according to provisional Eurostat data, which was 2.5mn t lower than a year earlier. This was the largest year-on-year decline in EU receipts since September 2016, when arrivals dropped by nearly 3mn t on the year to 8.7mn t.
June imports were also down from 6.5mn t the previous month, which was itself an 18-year low.
Coal-fired power generation has come under heavy pressure from highly competitive natural gas prices in 2019, with coal burn across Germany, Spain, the UK and France falling to as low as 3.2TWh in June and to a total of 43TWh in the first seven months of the year, down from 71.9TWh a year earlier and a three-year average of 110.2TWh in the first seven months in 2015-17.
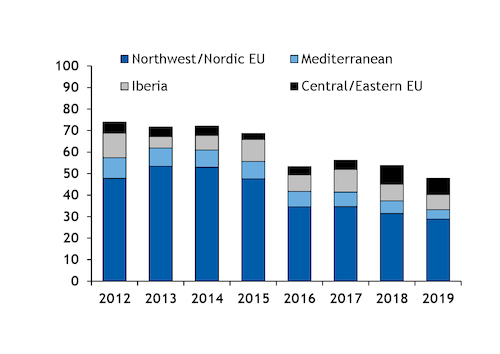
Aggregate coal burn was 22.5TWh lower on the year in January-June, which is equivalent to around 8.5mn t of 5,700 kcal/kg coal burn in 40pc-efficient coal-fired plants. Net imports to northwest Europe — Germany, France, the UK, Ireland and Benelux — were down by 2.3mn t on the year at 27mn t in January-June, with flows to Iberia and the Mediterranean down by a further 2.2mn t to 11.5mn t, suggesting a sizeable stock build across EU markets in the first half of 2019.
Port stocks in the Amsterdam-Rotterdam-Antwerp (ARA) region have been close to 7mn t for most of the year and consistently higher than the 2014-18 seasonal norm.
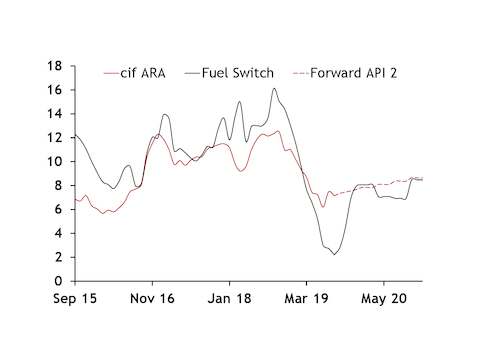
Day-ahead gas prices in Germany have fallen sharply in 2019 and have been weak enough to allow even low-efficiency combined-cycle gas turbine units to compete with 40pc-efficient coal-fired plants in the past three months. On 19 August, the cif ARA physical spot benchmark was around €2.85/MWh ($22/t)higher than the fuel-switch ceiling at which a 40pc-efficient coal-fired plant is at parity with a 45pc-efficient gas-fired unit.
Competitive gas prices for thermal generation — driven by unseasonably full storage sites and a sharp increase in LNG imports — have helped gas displace coal for thermal power generation in recent months. Coal burn in Germany, Spain, the UK and France fell by 9TWh on the year in the second quarter and by 4.1TWh in July, while gas burn in the same markets rose by nearly 14TWh in the second quarter and by almost 8TWh in July. This reduced coal's share of thermal generation to 12pc in April-July, from 22pc a year earlier.
And forward prices suggest that gas will continue to take a share from coal for the rest of the year. The API 2 fourth-quarter swap was €1.12/MWh ($8.68/t) higher than the ceiling at which 40pc coal-fired plants can compete with 55pc gas-fired units on 19 August. Last year spot coal prices were on average €2.69/MWh lower than the same coal-gas fuel switch threshold during the fourth quarter and coal accounted for around 27pc of all thermal generation in Germany, Spain, the UK and France.
Italy was the single biggest driver of the 5.9mn t drop in net EU coal imports in January-June, with receipts down by nearly 1.6mn t to 3.7mn t. Poland, France, the UK and Ireland have also dragged the total down, importing 0.8mn-1.2mn t less apiece. Arrivals to Germany and the Netherlands have partly offset the overall trend, with receipts up by 382,000t and 187,000t, respectively, to 5.9mn t and 15.7mn t.
Russian supply to the EU fell by less than 800,000t on the year in the first half of 2019 to 27.2mn t, boosting the country's share of EU imports by five percentage points to 57pc. Imports from the US and Colombia fell by 3.9mn t and 3.6mn t, respectively, accounting for much of the overall decline in thermal coal receipts in January-June.