It will take months to recover from lost production as extensive roadblocks aggravate the country's supply crunch, writes Daniel Politi
Oil and gas producers are warning that a blockade of Argentina's Vaca Muerta shale region by healthcare workers will prevent them from meeting supply commitments and force the country to spend more on imports.
Around 30 roadblocks that are preventing access into and out of Vaca Muertain the southwest province of Neuquen have caused production losses of 3.5mn m³/d of natural gas and 10,000 b/d of crude, according to workers at one oil company operating in the area. The output cuts have increased from 2mn m³/d and 5,000 b/d days earlier and will balloon if the protests persist, producers warn.
The blockade, which began on 7 April, has paralysed 70 rigs, according to the latest estimates, including drilling and hydraulic fracturing equipment, up from 45 last week. Some companies are using helicopters to transport their workers or taking alternative routes, substantially increasing journey times.
Argentina will need to raise spending on imports to more than $200mn to make up the lost production, oil and gas chamber CEPH says, and that figure will increase by $13mn/d for as long as the protests continue. "The lost production will take months to recover due to the lack of availability of the equipment required to fracture wells," it says.
The union of private oil and gas workers representing private-sector employees in the provinces of Neuquen, Rio Negro and La Pampa is seeking a court injunction that would allow workers to enter and leave the acreage.
The striking healthcare workers are demanding pay increases against a backdrop of rising Covid-19 cases. More than 60,000 people have died from the virus in the country. The protesters have rejected the provincial government's latest offer of a 53pc salary increase, because it would be made in installments to March 2022, as well as an earlier offer of a 30,000 peso ($324) bonus, paid in three installments. Negotiations to end the blockade are continuing.
The protests risk undermining companies' efforts to fulfil supply commitments agreed under a new gas subsidy scheme designed to meet rising demand during the southern hemisphere winter. Industry executives had already complained that the subsidy was launched too late, leaving them with a narrow window to boost output. A shortfall would force the government to curtail gas supply to industry to meet residential demand, and increase fuel and LNG imports.
Scramble for deliveries
The protest comes as Argentina's state-owned Ieasa scrambles to secure LNG supplies for the winter. The firm is seeking an additional 10 partial cargoes for delivery in June-August to its 3.7mn t/yr Escobar import facility in Buenos Aires, only days after it closed a tender to buy 13 cargoes for delivery in May-August, at an average cost of $7.20/mn Btu. The latest tender is the firm's third in the past two months to buy multiple LNG cargoes. Ieasa bought 24 partial cargoes in March for delivery in April-August to Escobar at an average price of $6.50/mn Btu.
Downstream, 80 service stations in Neuquen and neighbouring Rio Negro are short of fuel because the roadblocks are hindering distribution, with state-controlled YPF's 25,000 b/d Plaza Huincul refinery in Neuquen unable to dispatch tankers. Fuel deliveries to the company's service stations in the south of the country must travel from its 189,000 b/d La Plata plant in Buenos Aires province or 105,000 b/d Lujan de Cuyo refinery in western Mendoza.
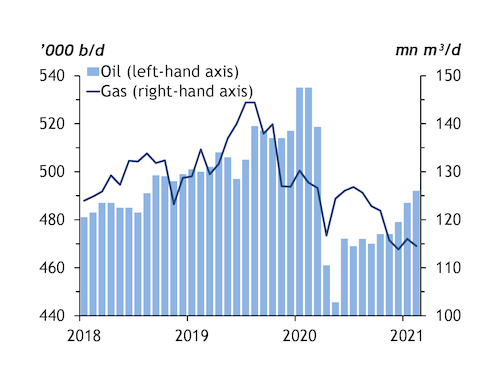
Argentina's oil and gas production was already flagging before the protests began. Crude output totalled around 490,000 b/d in the first two months of 2021, down by 5pc from a year earlier, energy secretariat data show. Gas flows fell by 11pc to 115mn m³/d over the same period.