From 1967 until the oil crisis of 1973 there were orders for about 80 very large crude carriers (VLCC) and 40 ultra large crude carriers (ULCC), according to engine manufacturer Wartsila. This boom was followed by the total collapse of the newbuild market for these tankers until the middle of the 1980s. Since then, over 400 VLCC have been ordered, but it took more than 20 years before the next ULCC contract was signed.
The new TI class of ULCCs were delivered in the early 2000s, but within a decade most had been converted to floating production, storage and offloading (FPSO) vessels (FSOs) for use in the Mideast Gulf and southeast Asia. Prizing quantity over flexibility, these ships were wider than the new Panama Canal locks (begun in 2007 and completed in 2016), and could not travel through the Suez Canal unless on a ballast voyage.
Their massive capacity of more than 3mn barrels of crude oil reflected climbing global oil demand – almost double what it was in 1973 – and China’s arrival as the world's largest importer of crude oil. Some forecasters now predict oil demand will peak in 2030, reducing the need for supertankers, but other forces have seen shipowners and others return to newbuilding markets for VLCCs in recent months.
Pandemics, infrastructure projects, price wars and actual wars have moved and lengthened trade flows in the last four years, making larger vessels more attractive because of their economies of scale. These have impacted the make-up of the global tanker fleet in other ways as well, such as prompting a small recovery in interest in small Panamax tankers, which have long been sliding out of existence.
The role of vessel size in tanker freight markets is sometimes underappreciated. In the wake of the G7+ ban on imports of Russian crude and oil and products, and attacks on merchant shipping in the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden by Yemen’s Houthi militants, flows of crude oil have had to make massive diversions. Russian crude oil is flowing now to India and China rather than to Europe, while Europe’s imports of oil, diesel and jet fuel from the Mideast Gulf are taking two weeks longer, going around the Cape of Good Hope to avoid Houthi attacks. This has pushed up tonne-miles – a measure of shipping demand – to record levels. Global clean Long Range 2 (LR2) tanker tonne-miles rose to a record high in May this year, data from analytics firm Kpler show, while tonne-miles for dirty Aframax tankers rose to a record high in May last year. It has also supported freight rates.
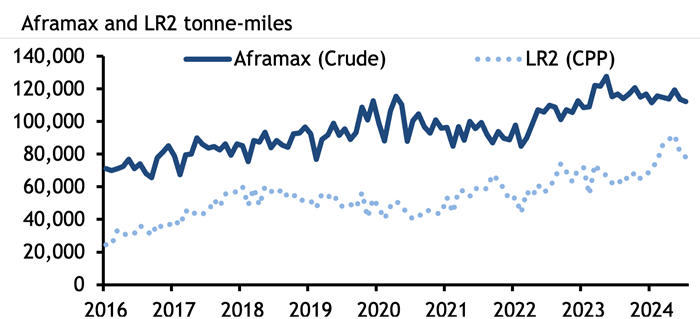
High freight rates have brought smaller vessels into competition with larger tankers, at the same time as long routes have increased the appeal of larger ships. The Atlantic basin appears to be key site for increases in production (from the US, Brazil, Guyana and even Namibia), and an eastward shift in refining capacity globally will further entrench these long routes and demand for economies of scale.
Aframax and LR2 tankers are the same sized ships carrying around 80,000-120,000t of crude oil or products. LR2 tankers have coated tanks, which allows them to carry both dirty and clean cargoes, and shipowners may switch their
LR2/Aframax vessels between the clean and dirty markets, with expensive cleaning, depending on which offers them the best returns. But an unusually high number of VLCCs – at least six – have also switched from dirty to clean recently. Shipowner Okeanis, which now has three of its VLCCs transporting clean products, said it had cleaned up another one in the third quarter.
A VLCC switching from crude to products is very rare. Switching to clean products from crude is estimated to cost around $1mn for a VLCC. It takes several days to clean the vessel's tanks, during which time the tanker is not generating revenue. But a seasonal slide in VLCC rates in the northern hemisphere this summer has made cleaning an attractive option for shipowners, while their economies of scale make the larger tankers more attractive to clean charterers as product voyages lengthen.
Argus assessed the cost of shipping a 280,000t VLCC of crude from the Mideast Gulf to northwest Europe or the Mediterranean averaged $10.52/t in June, much lower than the average cost of $67.94/t for shipping a 90,000t LR2 clean oil cargo on the same route in the same period. It is likely these vessels will stay in the products market, as cleaning a ship is a costly undertaking for a single voyage.
Typically, a VLCC will only carry a clean cargo when it is new and on its inaugural voyage, but just one new VLCC has joined the fleet this year, further incentivising traders to clean up vessels as demand for larger ones increases. This year has seen a jump in demand for new VLCCs, with 29 ordered so far. There were 20 ordered in 2023, just six in 2023 and 32 in the whole of 2021, Kpler data show. But the vast majority of these new VLCCs will not hit the water until 2026, 2027 or later because of a shortage of shipyard capacity.
Last year and 2024 also saw the first substantial newbuilding orders for Panamax tankers, also called LR1s, since 2017. Product tanker owner Hafnia and trader Mercuria recently partnered to launch a Panamax pool. The rationale may be that Panamax vessels can pass through the older locks at the Panama Canal, and so are not subject to the same draft restrictions imposed because of drought that has throttled transits and led to shipowners paying exorbitant auction fees to transit.
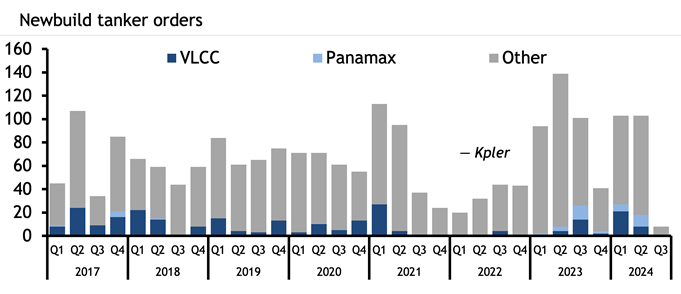
Aframaxes and MRs will remain the workhorses of crude and product tanker markets respectively, but the stretching and discombobulation of trade routes (which appear likely to stay) has already driven changes in which vessels are used and which are ordered. When these ships hit the water, they will join a tanker market very different to the one owners and charterers were operating in just four years ago.
Spotlight content
Related news
US utilities boost capex plans to records on AI demand
US utilities boost capex plans to records on AI demand
Houston, 27 February (Argus) — US utilities are boosting five-year spending plans to record heights to chase an unprecedented wave of data-center driven electricity demand. The sector outlined during the last batch of quarterly announcements hundreds of billions of dollars in investment for plans to support the power needs of artificial intelligence (AI) development that dwarf traditional load growth. Dominion Energy boosted its five-year capital expenditure (capex) plan to $65bn, citing accelerating demand in Virginia's "Data Center Alley." Southern Company lifted its program to $81bn, calling the moment a "watershed" for economic development across the Southeast as hyperscaler projects stack up. In Texas, Oncor raised its plan to a record $47.5bn, driven by a deluge of data center requests. Duke Energy raised its spending plan to $103bn, which the company said is the largest among regulated utilities. The moves underscore how the country's biggest data center markets are retooling their grids — adding transmission and gas-fired generation, hiking nuclear uprates, and extending the lives of coal assets facing closure — to keep pace with multi gigawatt loads that surpass existing capacity. The enormity of the investment figures and the scale of the projects call into question whether the forecasts are justified or even feasible. "Utilities generally adjust their large-load forecasts based on requests they are receiving from potential customers, so the increases from last year are well justified under a traditional load forecasting methodology," said Julia Hoos, head of USA East, at Aurora Energy Research. "That said, the more projects are asking to be interconnected, the more skeptical we have to be about them being realized." Pressure in the pipeline Gas and power utility Southern said its large-load pipeline in Alabama and Georgia grew to over 75GW. Texas distributor Oncor said its queue stood at an astonishing 225GW, or about a fifth of current US power generation capacity which is greater than the capacity of many industrialized nations like France and the UK. "Very few forecasts are taking into account the likelihood that large loads are shopping around with multiple utilities or that projects are often very delayed," said Hoos. Dominion, whose service territory covers the largest concentration of data centers in the world in northern Virginia, appeared to acknowledge such concerns by defining how it decided which companies qualify as pipeline projects. "Our forecasted data-center demand through 2045 is more than covered by existing signed ESAs (energy service agreements) and CLOAS (construction letter of authorizations)," said chief financial officer Steven Ridge. "By working diligently through the existing backlog and connecting the existing projects under construction, we'd achieve our demand forecast for the next approximately 20 years." The rapid expansion of data centers has ignited concerns that utilities will shift the cost of new power plants and transmission upgrades onto households, driving up monthly electric bills. Rising consumer frustration over higher electricity prices has made the issue a flashpoint for regulators and utility executives alike. President Donald Trump highlighted these concerns during his State of the Union speech, announcing, without details, that he is negotiating a ratepayer protection pledge that would require major technology firms to construct and fund their own dedicated generation. By Jasmina Kelemen Send comments and request more information at feedback@argusmedia.com Copyright © 2026. Argus Media group . All rights reserved.
US rPET demand under sustained pressure: PRC
US rPET demand under sustained pressure: PRC
Houston, 27 February (Argus) — Weak demand for US rPET dominated discussions at the Plastics Recycling Conference this week as buyers pull back, brands extend sustainability timelines, and low-priced imports and virgin PET intensify competition. Market deterioration continues as major recycler Evergreen Recycling, which filed for bankruptcy early last year, shut its plants in Clyde, Ohio, and Albany, New York, this week after its revolving credit lender moved to seize assets, forcing an immediate halt to operations, according to a 24 February Workers Adjustment and Retraining Notification (WARN) notice filed with the Ohio Department of Job and Family Services. Evergeen was one of the largest US rPET suppliers, and the plant closures reduce available recycling capacity. PET recyclers are facing mounting strain as rPET imports continue to displace US material, making it harder for recyclers to compete. "With the five closures, we've estimated about a 16pc capacity reduction, and it's exacerbating the problem," Laura Stewart, executive director of National Association for PET Container Resources (NAPCOR), told Argus in an interview at the conference, held in San Diego, California . "If domestic PET recyclers can't process bales and find strong end markets, it's going to be a challenge to keep the system going." Participants also noted that PET bottle recycling rates remain near 30pc nationwide and vary widely between states. California reclaimers described similar weak conditions, with persistently low prices failing to cover rising labor and processing costs. Several reclaimers said state-level subsidies are needed to maintain operations until demand improves, given the tightening margins across the market. "At the end of the day, you can't run a business on vibes. You've got to make payroll," said Paul Bahou, president of California-based Global Plastics Recyling. Bahou argued that subsidies are needed to ensure that the bottles that are collected can actually be recycled. "Collections is not recycling," Bahou said. "You need to take it [recycleable material] all the way." Bale pricing in California was described as stable but vulnerable to external shifts. Weakened purchasing activity from Mexico, traditionally a major buyer of US PET bales, has removed a key outlet for west coast supply, contributing to the soft demand environment. Conference discussions also highlighted structural limitations in the US system, including uneven access to recycling, competition with low priced virgin PET and limited domestic wash line capacity. The sudden loss of Evergreen's two plants intensified concerns that without stronger, more consistent end-market demand, US recyclers will continue to face financial pressure even as recycled content mandates expand. By Dona Davis Send comments and request more information at feedback@argusmedia.com Copyright © 2026. Argus Media group . All rights reserved.
China's GWM to build second car factory in Brazil
China's GWM to build second car factory in Brazil
Sao Paulo, 27 February (Argus) — Chinese automaker Great Wall Motor (GWM) will build a second car factory in Brazil, which could drive domestic flat steel demand up. GWM's new factory, in southeastern Espirito Santo state, will have a nameplate capacity of 200,000 vehicles/yr, four times larger than its first Brazilian plant , according to the state government. The facility is part of the company's R10bn ($1.9bn) investment plan in Brazil through 2032. GWM sells mostly electric vehicles (EVs) in Brazil, but it has a couple of internal combustion engine (ICE) models as well. It is still unclear which model the automaker will manufacture in the plant, but the Haval H4, a compact SUV, is a strong contender. Given the popularity of this car category in Brazil, demand for the H4 would likely be in line with the new plant's capacity. The H4 is sold in other Latin American countries as a hybrid vehicle under the name of Haval Jolion Pro. Since the factory will be built from scratch, it is difficult to pin an inauguration date as construction work in Brazil often faces delays. GWM has close ties with the Espirito Santo government, having used the state's main port, Vitoria, as an import hub for all the vehicles it brought from China to Brazil. GWM plant could drive domestic steel demand Construction is expected to use from 40,000-70,000 metric tonnes (t) of steel, according to the Espirito Santo government. Most of the flat steel used during the building phase will likely be sourced from domestic producer ArcelorMittal. The new factory aligns with the steelmarker's plans to build a cold-rolling mill in Tubarao — also in Espirito Santo — which is its largest plant in Brazil, the company told Argus . ArcelorMittal announced in 2025 a R4bn ($777.4mn) investment to boost steel output in Brazil, but it has yet to officially decide where to allocate the resources . The company expects to make a final decision by the end of the first quarter. The GWM project could signal that ArcelorMittal may ultimately favor Espirito Santo over expanding its Pecem plant, in northeastern Ceara state. Construction is also expected to use 200,000-350,000t of concrete. By Pedro Consoli and Isabel Filgueiras Send comments and request more information at feedback@argusmedia.com Copyright © 2026. Argus Media group . All rights reserved.
Venezuela reviewing latest ad-hoc oil contracts
Venezuela reviewing latest ad-hoc oil contracts
Caracas, 27 February (Argus) — Venezuela's state-owned oil firm PdV is reviewing 26 joint ventures granted from 2024-2025 to align them with changes to the hydrocarbons law or cancel them after the US has demanded reforms for investors. Now president Rodriguez began implementing new types of joint ventures, including some known as productive participation agreements (CPPs), after she took on the role of oil minister in October 2024 as part of her vice presidency. The arrangements could be retrofitted to match provisions under the recently modified hydrocarbons law, one PdV source told Argus , but more likely they may be cancelled. The 26 oil contracts granted after the ouster and arrest of former oil minister Pedro Tellechea in October 2024 and before the US seized former Venezuela leader Nicolas Maduro on 3 January are being reviewed, the PdV source said. Of those, 13 are CPPs. The PdV source said the US is pressuring Rodriguez to end those contracts since most of the other partners are non-US or little-known entities. "I think they will all be suspended," the source said. "What the Americans have told us is [any deals] need to be authorized by us." Rodriguez and Maduro granted the 26 deals in the two years but provided few public details. Even after Maduro was arrested on 3 January, Rodriguez still described the CPPs as a way forward to increase Venezuelan oil production. But once the law was modified the government and its partners were granted six months to adopt the contracts to the new law or cancel them. Sources say the arrangements were doomed to fail, since they were laboring from the beginning under the weight of US sanctions that are only now beginning to be lifted. "She granted two dozen contracts, but only five of those ... are in actual production", a former Venezuelan oil minister said. "Eliminating or retooling those contracts will have zero impact on production." Retooling those agreement or granting new ones may instead help to increase Venezuela's production from its plateau of about 1mn b/d in recent months. By Carlos Camacho Send comments and request more information at feedback@argusmedia.com Copyright © 2026. Argus Media group . All rights reserved.




