From 1967 until the oil crisis of 1973 there were orders for about 80 very large crude carriers (VLCC) and 40 ultra large crude carriers (ULCC), according to engine manufacturer Wartsila. This boom was followed by the total collapse of the newbuild market for these tankers until the middle of the 1980s. Since then, over 400 VLCC have been ordered, but it took more than 20 years before the next ULCC contract was signed.
The new TI class of ULCCs were delivered in the early 2000s, but within a decade most had been converted to floating production, storage and offloading (FPSO) vessels (FSOs) for use in the Mideast Gulf and southeast Asia. Prizing quantity over flexibility, these ships were wider than the new Panama Canal locks (begun in 2007 and completed in 2016), and could not travel through the Suez Canal unless on a ballast voyage.
Their massive capacity of more than 3mn barrels of crude oil reflected climbing global oil demand – almost double what it was in 1973 – and China’s arrival as the world's largest importer of crude oil. Some forecasters now predict oil demand will peak in 2030, reducing the need for supertankers, but other forces have seen shipowners and others return to newbuilding markets for VLCCs in recent months.
Pandemics, infrastructure projects, price wars and actual wars have moved and lengthened trade flows in the last four years, making larger vessels more attractive because of their economies of scale. These have impacted the make-up of the global tanker fleet in other ways as well, such as prompting a small recovery in interest in small Panamax tankers, which have long been sliding out of existence.
The role of vessel size in tanker freight markets is sometimes underappreciated. In the wake of the G7+ ban on imports of Russian crude and oil and products, and attacks on merchant shipping in the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden by Yemen’s Houthi militants, flows of crude oil have had to make massive diversions. Russian crude oil is flowing now to India and China rather than to Europe, while Europe’s imports of oil, diesel and jet fuel from the Mideast Gulf are taking two weeks longer, going around the Cape of Good Hope to avoid Houthi attacks. This has pushed up tonne-miles – a measure of shipping demand – to record levels. Global clean Long Range 2 (LR2) tanker tonne-miles rose to a record high in May this year, data from analytics firm Kpler show, while tonne-miles for dirty Aframax tankers rose to a record high in May last year. It has also supported freight rates.
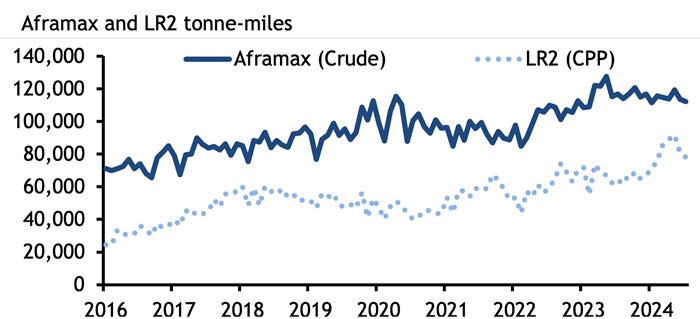
High freight rates have brought smaller vessels into competition with larger tankers, at the same time as long routes have increased the appeal of larger ships. The Atlantic basin appears to be key site for increases in production (from the US, Brazil, Guyana and even Namibia), and an eastward shift in refining capacity globally will further entrench these long routes and demand for economies of scale.
Aframax and LR2 tankers are the same sized ships carrying around 80,000-120,000t of crude oil or products. LR2 tankers have coated tanks, which allows them to carry both dirty and clean cargoes, and shipowners may switch their
LR2/Aframax vessels between the clean and dirty markets, with expensive cleaning, depending on which offers them the best returns. But an unusually high number of VLCCs – at least six – have also switched from dirty to clean recently. Shipowner Okeanis, which now has three of its VLCCs transporting clean products, said it had cleaned up another one in the third quarter.
A VLCC switching from crude to products is very rare. Switching to clean products from crude is estimated to cost around $1mn for a VLCC. It takes several days to clean the vessel's tanks, during which time the tanker is not generating revenue. But a seasonal slide in VLCC rates in the northern hemisphere this summer has made cleaning an attractive option for shipowners, while their economies of scale make the larger tankers more attractive to clean charterers as product voyages lengthen.
Argus assessed the cost of shipping a 280,000t VLCC of crude from the Mideast Gulf to northwest Europe or the Mediterranean averaged $10.52/t in June, much lower than the average cost of $67.94/t for shipping a 90,000t LR2 clean oil cargo on the same route in the same period. It is likely these vessels will stay in the products market, as cleaning a ship is a costly undertaking for a single voyage.
Typically, a VLCC will only carry a clean cargo when it is new and on its inaugural voyage, but just one new VLCC has joined the fleet this year, further incentivising traders to clean up vessels as demand for larger ones increases. This year has seen a jump in demand for new VLCCs, with 29 ordered so far. There were 20 ordered in 2023, just six in 2023 and 32 in the whole of 2021, Kpler data show. But the vast majority of these new VLCCs will not hit the water until 2026, 2027 or later because of a shortage of shipyard capacity.
Last year and 2024 also saw the first substantial newbuilding orders for Panamax tankers, also called LR1s, since 2017. Product tanker owner Hafnia and trader Mercuria recently partnered to launch a Panamax pool. The rationale may be that Panamax vessels can pass through the older locks at the Panama Canal, and so are not subject to the same draft restrictions imposed because of drought that has throttled transits and led to shipowners paying exorbitant auction fees to transit.

Aframaxes and MRs will remain the workhorses of crude and product tanker markets respectively, but the stretching and discombobulation of trade routes (which appear likely to stay) has already driven changes in which vessels are used and which are ordered. When these ships hit the water, they will join a tanker market very different to the one owners and charterers were operating in just four years ago.
Spotlight content
Related news
LNG carriers steer clear of strait of Hormuz
LNG carriers steer clear of strait of Hormuz
London, 28 February (Argus) — At least nine LNG carriers today changed course away from the strait of Hormuz, although the number may be even higher as AIS transponder interference in the region has obfuscated shiptracking. Of the nine, seven were empty heading towards the Mideast Gulf to load. Two recently loaded and turned away from the strait today (see table) . The laden carriers are operated by state-owned QatarEnergy (QE), by far the largest LNG producer in the Mideast Gulf. No LNG carriers were approaching the strait as of 19:00 GMT, shiptracking data from both Kpler and Vortexa show. The last laden LNG carrier to pass through Hormuz was the 155,000m³ Gaslog Shanghai at 11:00 GMT. The strait of Hormuz stands between 82.6mn t/yr of LNG supply — or 291mn m³/d of pipeline gas equivalent — and international markets. Some 19pc of the world's LNG transited the waterway from the Mideast Gulf last month, Kpler data show. Many carriers in the Mideast Gulf have had AIS transponder interference, adding to vessel traffic danger. The United Kingdom Maritime Trade Operations (UKMTO) said today it had received reports from vessel officers of broadcasts informing that the strait has been closed, although it said the reports could not be independently verified. Turkey and Egypt in the fallout Beyond a potential Hormuz closure, regional conflict could spur LNG demand in Turkey and Egypt. Egypt last reported Israeli gas imports at 681mn m³, or 22.7mn m³/d, in November. Israel has probably halted gas exports to Egypt as Israel's Karish and Leviathan gas fields have gone off line .This led to a stop in flows to Egypt in 2025. Egyptian LNG demand could rise to a rate of 6.4mn t/yr, or one LNG cargo every four days. This could test Egyptian import capacity, and some cargoes could be imported through Jordan. But near-term regasification capacity will improve next week, as the 160,000m³ Energos Eskimo floating storage and regasification unit (FSRU) is today heading to Egypt from a maintenance shipyard in Turkey. Iran exported 576mn m³, or 18.6mn m³/d, of gas to Turkey in December. Should Tehran halt gas exports then Turkish demand could rise to a rate of 5.3mn t/yr of LNG, or one cargo every five days, to replace the lost Iranian gas. By Martin Senior Hormuz LNG carrier diversions Carrier Diversion time (GMT) Status Al Sahla 10:00 Loaded Mraikh 11:00 Loaded LNG Abuja 9:00 Emtpy Al Marrouna 12:30 Empty Aseem 9:45 Empty Broog 9:15 Empty Onaiza 9:45 Empty Taitar No.3 10:00 Empty Cool Explorer 6:00 Empty — Kpler, Vortexa Send comments and request more information at feedback@argusmedia.com Copyright © 2026. Argus Media group . All rights reserved.
Mideast Gulf ships receive Hormuz 'ban' message: UKMTO
Mideast Gulf ships receive Hormuz 'ban' message: UKMTO
London, 28 February (Argus) — Multiple vessels operating the Mideast Gulf have received radio transmissions stating that the strait of Hormuz has been closed, the UK Maritime Trade Operations agency said today. The UKMTO said broadcasts or statements indicating a closure are not legally binding and it advised vessels to transit with caution. The reports from vessels were not independently verified, UKMTO said. An unverified transmission shared with Argus stated: "From now on the strait of Hormuz is banned for all ships… No ship [of any type] is not allowed to pass [through] the strait of Hormuz." The message was said to be broadcast from the Iranian-flagged Bahram 1, whose location was last shared in 2024. The strait of Hormuz is international water, overlapped by the territories of Iran and Oman. While coastal state sovereignty exists in territorial waters, it cannot be used to bar passage of ships. The US military today begun "major combat operations" in Iran following co-ordinated Israeli strikes, marking the most significant escalation in years in the oil-rich Mideast Gulf region and sharply raising the risk of oil and gas supply disruptions. Marine traffic through the Gulf remains high, ship tracking platforms show, although a handful of laden and ballast tankers operating in the area, mostly bound for Asia-Pacific destinations, have performed U-turns. By Melissa Gurusinghe and Andrey Telegin Send comments and request more information at feedback@argusmedia.com Copyright © 2026. Argus Media group . All rights reserved.
Egypt urea sold higher after US, Israel attack on Iran
Egypt urea sold higher after US, Israel attack on Iran
Amsterdam, 28 February (Argus) — Egyptian fertilizer producer Mopco has sold 6,000t of granular urea at $505/t fob, while fellow supplier Alexfert concluded 6,000t at $495/t fob. Both cargoes are for loading in March and likely to be for European markets. Argus assessed granular urea at $480-485/t fob Egypt to Europe on 27 February. Prices have jumped after the US military today began "major combat operations" in Iran following co-ordinated Israeli strikes. Iran has responded by firing missiles towards Israel and US military bases across the region. Multiple Egyptian urea producers have reported no change in gas supply to plants in the country so far in the aftermath of the attacks. But Israel's energy ministry has instructed Greek firm Energean to temporarily suspend production at its offshore Karish gas field "following the recent geopolitical escalation in the region", the company told Argus . A source said Israel has also ordered the closure of the country's largest gas field, Leviathan, as a precautionary measure. Leviathan operator Chevron referred questions to the energy ministry. There is no indication of the status of Chevron's other gas field in Israel, Tamar. Gas flows from Israel to Egypt were cut in the wake of the conflict between Israel and Iran in mid-June last year, which resulted in all Egyptian urea production being taken offline, sending urea prices into Europe soaring. The Middle East is the largest urea export region globally and ships around 20mn t/yr, of which Iran accounts for about a quarter. Egypt typically exports around 4mn t/yr of urea, mostly to Europe. Major urea producers in the Middle East host US forces, including Saudi Arabia, Qatar, the UAE, Bahrain and Oman. By Harry Minihan Send comments and request more information at feedback@argusmedia.com Copyright © 2026. Argus Media group . All rights reserved.
US, Israel launch major attack on Iran: Update
US, Israel launch major attack on Iran: Update
adds details throughout Dubai, 28 February (Argus) — The US military today began "major combat operations" in Iran following co-ordinated Israeli strikes, marking the most significant escalation in years in the oil-rich Mideast Gulf and sharply raising the risk of oil and gas supply disruptions. Iran has responded by firing missiles towards Israel and US military bases across the region. "A short time ago, the United States military began major combat operations in Iran. Our objective is to defend the American people by eliminating imminent threats from the Iranian regime," President Donald Trump said. The US Department of Defense has codenamed the attack "Operation Epic Fury". Trump said the US would destroy Iran's missile inventory and industry and "annihilate their navy", reiterating that Tehran "will never have a nuclear weapon". He told members of Iran's Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) and security forces to "lay down your weapons and have complete immunity or face certain death". Israeli prime minister Benjamin Netanyahu said the joint US-Israeli attack on Iran "will create the conditions for the brave Iranian people to take their destiny into their own hands". "The time has come for all sections of the people in Iran … to remove the yoke of tyranny … and bring a free and peace-loving Iran," Netanyahu said in a televised statement. Videos circulated on social media indicated explosions in Tehran shortly before Trump's remarks. Israel earlier confirmed it had launched what it described as a "pre-emptive attack" against Iran, and defence minister Israel Katz declared a national state of emergency and warned of expected retaliatory missile and drone strikes. Israel closed its airspace to civilian traffic, suspended non-essential activities and instructed citizens to remain near shelters. Iran also closed its airspace, and several commercial airlines have diverted or cancelled flights to the region. Bahrain said the service centre of the US Fifth Fleet had been subjected to a missile attack. Video footage showed a thick grey plume of smoke rising in Manama. The UAE, Kuwait and Qatar said their air-defence systems intercepted Iranian missiles that violated their airspace. Saudi Arabia strongly condemned what it called "blatant Iranian aggression" and a dangerous violation of the sovereignty of other Mideast Gulf countries. All Mideast Gulf oil producers host US forces, including Saudi Arabia, Qatar, the UAE, Bahrain, Oman and Kuwait. Meanwhile, EU high representative for foreign affairs Kaja Kallas said the bloc's "Aspides" naval mission "remains on high alert in the Red Sea and stands ready to help keep the maritime corridor open." The strikes today signal the collapse of renewed US-Iran nuclear negotiations held in Switzerland this week. Trump said the military operation began after Iran refused to renounce nuclear weapons ambitions. Tehran has repeatedly denied seeking atomic weapons and warned it would retaliate against US bases in the Mideast Gulf region if attacked. It launched missiles towards the US Al Udeid air base in Qatar during a 12-day conflict in June 2025, after US and Israeli strikes on Iranian nuclear facilities. Oil markets were already pricing in some geopolitical risk ahead of the escalation, with front-month Ice Brent crude trading near $73/bl on Friday, its highest since July. An outright war between the US-Israel and Iran risks disruption to shipping lanes and flows through the strait of Hormuz, through which around 20pc of global oil supply and a significant share of LNG exports transit. Opec+ ministers of the core group of eight are scheduled to meet on Sunday to review production policy for the month of April. Delegates had been weighing a modest supply increase from April, but the escalation introduces new uncertainty over supply balances and the group's strategy. The US has significantly expanded its military presence in the Middle East in recent weeks, including air and naval assets, ahead of the breakdown in talks. Trump in his statement today acknowledged the risk of US casualties but said the operation was necessary to prevent Iran from acquiring nuclear weapons. By Bachar Halabi Send comments and request more information at feedback@argusmedia.com Copyright © 2026. Argus Media group . All rights reserved.




