The 25pc steel tariff implemented by the US in March via Section 232 is having a huge impact on the global ferrous market.
Much has been made of the precipitous rise in US hot rolled coil pricing to over $900/st. Mills are making considerable margins, domestic production is coming back online and regaining market share from imports.
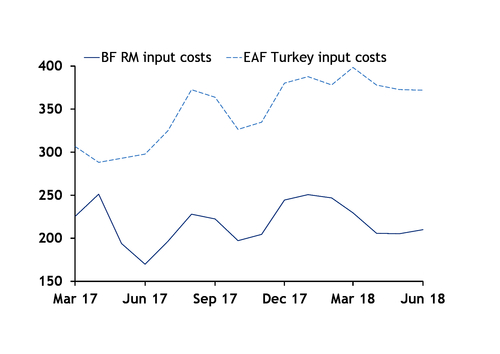
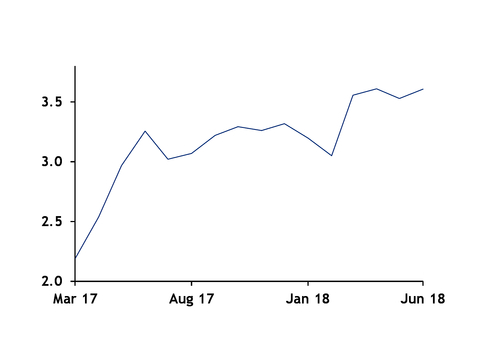
But there are more nuanced impacts: scrap prices, already supported by Chinese environmental policies, have rallied on surging US steel prices and the prospect of higher steel production. This has significantly altered the relative economics of electric arc furnaces (EAF) and integrated mills. The spread between Chinese imported iron ore costs and Turkish imported scrap — both price-making markets for the respective commodities — has ballooned recently. The difference between Turkish imported heavy melting scrap 1/2 (80:20) and Chinese 62pc Fe ore imports was $280.30/t yesterday, with scrap at $342.50/t and iron ore $62.20/t, according to Argus data. A ratio over 5:1 is huge, with 3.5/4:1 more typical. As a result of rising scrap demand and the 232-related price-bump, input costs for EAFs are now about 70pc higher than combined ore and coal costs for a blast furnace.
US influence
The US is a key determinant of steel scrap pricing as the biggest single-country exporter and a large user itself. The run-up in domestic steel pricing post-232 has buoyed scrap, as has the spectre of increased production. Investment bank Jefferies says US crude steelmaking output will rise by 9.6mn t between now and 2020.
Scrap-intensive electric arc furnace production accounts for 70pc of the US market, having wrested significant share from less efficient integrated producers over the last 10 years. The strength of the US market has led to atypical differentials between scrap grades. Shredded material, typically selling at a $5/mt premium to HMS 80:20 in the bellwether Turkish market, was commanding $15/mt more, alongside bonus and busheling, during May and June. Shredded demand from other markets such as Pakistan, Bangladesh and Southeast Asia played a part in this, alongside Section 232. In the latest Turkish deals, the shredded/80:20 spread has narrowed to $10/mt, but primes are still trading at more significant premiums.
Weakening Chinese steel exports have also lifted scrap demand by increasing EAF production elsewhere. At the same time, China's basic oxygen furnaces are also increasing scrap consumption at the expense of sinter fines amid Beijing's sharper pollution focus. The elevated scrap-to-ore price ratio may be partly structural for these China-led reasons, with stricter environmental policies likely here to stay. If China commissions more EAFs, which is likely, scrap demand from the world's largest steel market will grow considerably. But its reservoir of arising scrap may outstrip demand, resulting in significant exports which could alter global pricing dynamics.
Turkish struggles
Surging input costs are a considerable disadvantage to Turkey and its preponderance of EAFs, although the cost-base is always higher for the nimbler mini-mill. Turkey is struggling to sell into markets, such as Asean, which had been key export locations amid a contraction in demand from typical buyers in the US and Middle East. European shipments have bucked this trend. The EU took 274,955t of Turkish rebar over the first four months of this year, compared with 75,399t last year. But concern over safeguarding will probably see this flow slow in second quarter data. The European Commission began investigating potential safeguarding after the US announced Section 232, and it was recently announced a preliminary measure would be implemented.
Turkey's weakening currency is also creating issues, as continuous increases in lira-denominated rebar prices are not aiding demand during political and economic uncertainty at home. President Erdogan's greater influence over monetary policy is spooking investors and causing wild forex gyrations.
Turkey has started buying more third-country slab and billet this year, as it has been more economical than melting scrap — as was the case in 2015, when Turkish mills imported around 16 mn t of scrap, compared with around 24 mn t last year, meaning the country was a net steel importer.
Either Turkey is going to be turning more heavily to imported basic oxygen furnace-produced semis, or scrap prices are likely to fall. As it happens, with the US steel market stabilising amid seasonally slower demand, merchants are beginning to grow concerned over the direction of domestic settlements for August and September. One trader using the London Metal Exchange contract said $300/mt would be achievable for Turkish 80:20 imports soon.