Sharp increases in EU emissions trading system (ETS) allowance values in recent sessions have worsened market conditions for German coal-fired power generation for next year, with around 46pc of the fleet priced out of the base-load market.
The outlook for medium-efficiency coal-fired power plants in Germany for the second and third year ahead also weakened.
EU ETS market prices have increased sharply in recent sessions, with the December 2021 contract closing at €29.99/t of CO2 equivalent (CO2e) yesterday, up by 30pc compared with a month ago, Argus data show.
The German front-year base-load contract is highly correlated to the European carbon market given its carbon-intensive energy mix, but its gains were slower, up by 12pc since 8 June to €43.35/MWh in yesterday's session. Slower gains in year-ahead cif ARA coal swaps, up by 7pc during the same period to €7.04/MWh yesterday, have failed to offset faster gains in carbon and power costs.
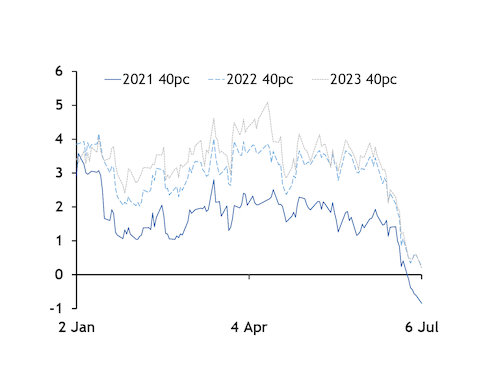
Clean dark spreads for a 40pc-efficient unit for 2021 closed yesterday's session at minus €0.80/MWh, the lowest level ever recorded for these units. Spreads for these units declined from €1.65/MWh a month ago and have been in negative territory since 29 June.
During the same period last year, equivalent spreads for 2020 base load — the then front year — were at €5.98/MWh, and expired at €0.89/MWh on 31 December.
Germany has around 17.2GW of operational coal-fired power plants, according to most recent data from Bnetza, including the recently launched 1.1GW Datteln 4 unit. An analysis of official and assumed efficiencies suggest that around 8-9GW of coal-fired units have an efficiency of 40pc or below, meaning almost half of Germany's coal fleet could be out of the German merit order next year on a base-load basis.
Coal-fired operators could find an incentive to run during peak-load hours as spreads closed at €8.80/MWh in yesterday's session.
Medium and high-efficiency coal-fired units have already been unprofitable to operate on a base-load basis so far this year. Working day-ahead clean dark spreads have averaged minus €6.48/MWh for a 40pc-efficient unit and minus €2.05/MWh for a 46pc-efficient plant.
On a day-ahead hourly basis, only hour 19 has seen positive clean dark spreads, at an average of €0.65/MWh so far this year for a plant with an efficiency of 40pc. Spreads have averaged higher for the same hour in the intra-day market at €1.01/MWh.
Coal-fired generation has averaged 3.26GW this year so far and made up 5.9pc of the German generation mix, compared with 9.5pc in 2019, given higher renewables output, lower power demand and better market conditions for gas-fired generation, which is well embedded in the German merit order.
Spreads for 2022-23
Clean dark spreads for the second and third year ahead have also narrowed in recent sessions, recording new lows and moving closer to zero.
Clean dark spreads for 2022 closed at €0.23/MWh yesterday — the lowest level ever recorded for this period. Clean dark spreads for 2023 base load narrowed to €0.18/MWh, a new low for this period too.
Germany is expected to start closing coal-fired plants from next year. The Bundestag and Bundesrat passed the coal and lignite phase-out law last week.
The first tender for the closure of 4GW of capacity will be held in September, with successful plants being notified in December. Operators will have seven months to decommission their plants from the moment they are notified, meaning the first closures will happen in summer next year.
On top of lower coal-fired capacity, Germany is expected to start 2022 with 4GW less nuclear capacity, under the nuclear phase-out law.
Germany expects to start 2023 with 15GW of coal-fired capacity, end 2029 with 8GW and reach zero by 2038 at the latest.
Lignite
The increase in EU ETS allowances has also weighed on the future profitability of lignite-fired plants in the near term, with around 38.7pc of the fleet priced out on a base-load basis next year.
Clean lignite spreads for a 34pc-efficient unit for 2021 base-load delivery closed at minus €0.66/MWh yesterday, based on lignite costs of €2.85/MWh. These units entered unprofitable territory for the first time last week.
Market conditions for lignite burn for the power sector have also been weaker this year. Working day-ahead clean lignite spreads have averaged minus €7.35/MWh for a 34pc unit, with even 43pc sites struggling, with spreads averaging minus €0.07/MWh so far this year.
Germany has around 17.9GW of operational lignite-fired capacity, out of which 6.97GW relates to units with an assumed efficiency of 34pc or lower, Argus estimates.
Under the most recently approved coal and lignite phase-out law, the first unit will close by the end of this year — RWE's 300MW Niederaussem D. The plant generated just 0.03TWh of power in June, according to Fraunhofer ISE data.
Around 910MW of capacity will close by the end of 2021. The country aims to have 15GW by the end of 2022, 9GW by the end of 2029 and zero by 2038 at the latest.