Capacity restrictions cut South Korean coal-fired generation on the year for the 12th consecutive month in April, but an increasingly wide nuclear shortfall early this summer and the start-up of new coal-fired units could support output in the near term.
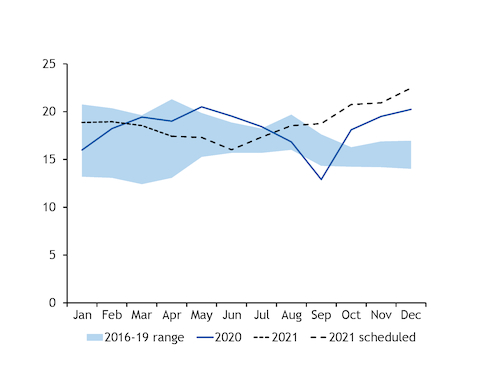
National power generation grew by 1.9GW on the year to 60.6GW in April while nuclear output fell by 1.6GW to 17.4GW, as unplanned outages at the Kori 2, Hanul 1 and Hanul 2 reactors cut availability by around 1.4GW compared with previous expectations.
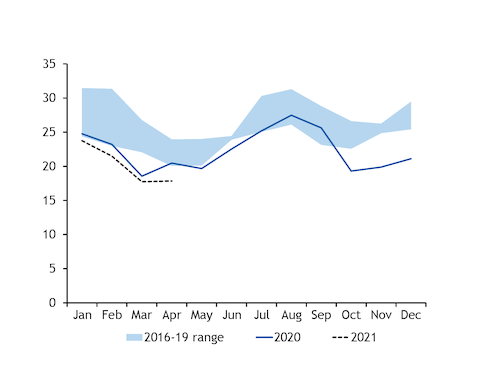
This increased South Korea's reliance on fossil fuels, but coal-fired generation still fell because of greater capacity restrictions, driving a particularly sharp rise in gas-fired generation.
State-owned Kepco's available coal-fired capacity fell by 3.7GW on the year in April, according to Argus analysis, with output declining by around 3.2GW as a result. This was partly offset by a rise in coal-fired generation among private-sector utilities, which limited the overall drop in coal burn to 2.6GW.
The government has asked Kepco utilities to voluntarily reduce their coal-fired generation in 2021 to reduce overall emissions. In April, 1.6GW of the 3.7GW year-on-year increase in restrictions was down to voluntary suspensions.
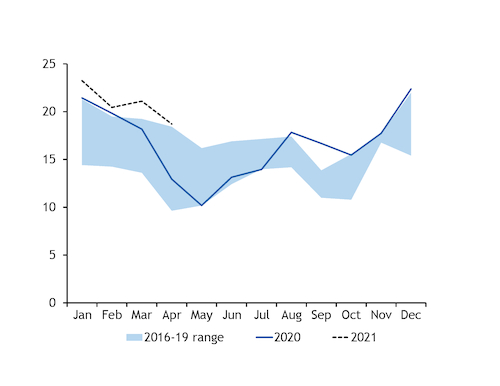
With coal constrained, the country's gas-fired generation rose strongly by 5.8GW on the year to 18.7GW to meet electricity demand.
Kepco coal-fired availability has remained below 2020 levels since April, but overall coal burn is likely to still have been broadly in line with last year in May-June because of a shortfall in nuclear availability and the commissioning of new coal-fired units.
Nuclear schedules suggest that generation may have fallen by around 3.2GW on the year in May, while the continuing outage at Shin Kori 4 looks likely to take 1.4GW of capacity out for the whole of June and depress output by 3.5GW compared with a year earlier.
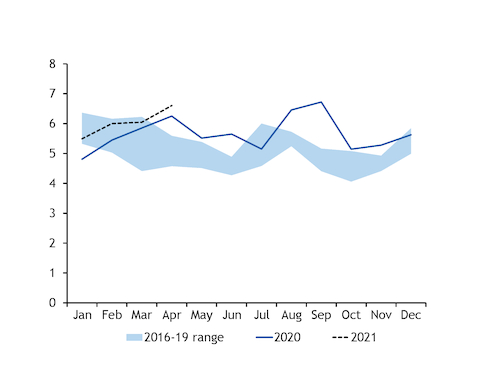
At the same time, national power demand has recovered from last year's pandemic-induced lows with total generation needing to grow by around 2.9GW on the year in May and 800MW in June, according to Argus analysis.
State-owned gas supplier Kogas' sales to the power sector grew by nearly 80pc on the year in May, which suggests continued growth in gas-fired generation, with coal burn likely to be broadly flat with last year in May-June as new private-sector coal-fired units offset the impact of greater restrictions across the Kepco fleet.
The 1.04GW Goseong 1 coal-fired unit is understood to have begun operations in May, with the 1GW Shin Seocheon 1 and 1.04GW Goseong 2 scheduled to start up in June and October, respectively.
Coal-fired generation may begin to climb on the year in July and August, as recent nuclear maintenance extensions could increase the market's reliance on fossil fuels during the peak cooling period.
A long-term outage at Hanbit 5 has been extended by around two months to 28 September, while the end of maintenance at the Shin Wolsong 1 reactor was pushed back by a month to 26 July, according to operator Korea Hydro and Nuclear Power. Nuclear availability is now expected to average 17.3GW in July and 18.5GW in August.
But nuclear availability is still scheduled to grow strongly on the year in September-December to an average of around 20.7GW, which could weigh on generation from fossil fuels later in the year. This could be particularly weak for power-sector gas demand, as rising oil-linked LNG term contracts support domestic gas prices and potentially help to extend coal's cost advantage for power, which was largely wiped out during the pandemic.