Global steam cracker operating rates have been trending downward from 89pc in 2018 to 79pc in 2023, driven by the combination of high-capacity increase and slower economic growth in recent years.
In Argus's latest Ethylene Analytics, a recovery is forecast to take place in the coming years as the recent wave of new capacity cools off, absorbing demand growth before the second wave of capacity addition outgrows demand from 2027-2029. This recovery is based on a modelled assumption of modest growth in the global economy and a slowdown in capacity expansion. Historically, olefins demand growth has trended in line with GDP growth on a global basis; in recent years this relationship has disconnected. This was a result of the imbalance between the service and manufacturing industries, but we anticipate the trend will revert sooner or later moving forward.
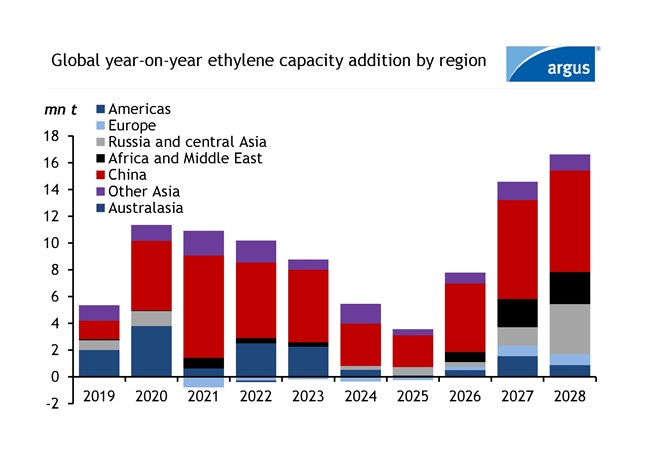
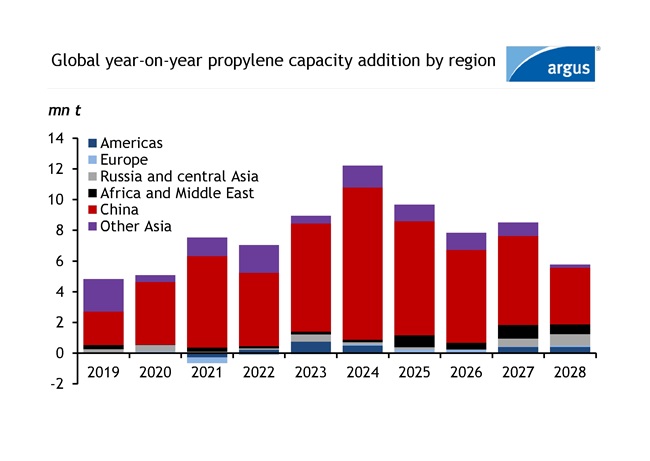
The petrochemical industry is experiencing high levels of upcoming capacity over the next five years. On a global level, ethylene and propylene capacity is expected to increase by 47.4mn t (4pc) and 44.0mn t (5pc), respectively, over the next five years while global capacity growth from 2018 to 2023 averaged at 4.5pc/yr for both ethylene and propylene. Most investment in ethylene production has gone into steam crackers where ethylene is the main product and propylene is produced as a co-product. Propylene will see a high-capacity increase from not only steam crackers but also from propane dehydrogenation (PDH) projects, which will delay the recovery of global propylene operating rates.
The first wave of ethylene capacity addition is cooling off, but a second wave is expected to kick off in 2026. However, propylene is currently undergoing its wave of capacity addition before seeing a slowdown from 2028 onward. On the propylene side of the olefins chain, 50pc of the upcoming capacity will come from PDH, 34pc from steam crackers and the rest will be a combination of sources from refinery, coal, and methanol.
Operating rates in all regions are being negatively impacted by the combination of high-capacity increase and slower global economic growth. Olefins demand has experienced slower growth over the past two years, with negative growth in 2022 as a result of high inflation and lower consumer spending.
Based on current market fundamentals there have been project delays across most regions and also rationalisation from uncompetitive units. With steam crackers running at lower-than-normal operating rates, rationalization of capacities is a significant unknown as what assets are to shut down are dependent on many factors such as company financials, politics, and integration factors. This makes the rationalization of specific units tough to predict.
As western nations are experiencing slower GDP growth, developing nations will be the key regions for olefins growth. We are seeing a slowdown in Chinese and northeast Asian GDP, but south Asian GDP has been holding strong. Polymer demand, which accounts for more than half of olefins consumption will be the main driver of olefins demand (65pc of ethylene gets consumed into PE and 71pc of propylene gets consumed into PP globally). From a supply perspective, 17pc (8mn t) of all upcoming cracker projects have yet to start construction, which will give operating rates a boost if delayed. Given the slowdown in global economic growth in the past two years, high interest rates, and inflation, the overall outlook is fairly bearish. Consumer spending, household disposable income, economic growth, project timelines, and rationalization from uncompetitive production facilities will be the main indicators of how quickly it will take for operating rates to recover.
Current announced projects
In the past five years, most steam cracker capacity increases took place in China and the trend is expected to persist over the next five years based on announced projects, but most regions are investing. Other Asian countries such as India, South Korea, Vietnam, and Indonesia are also investing. A total of 25.6mn t and 32.9mn t of ethylene and propylene capacity is expected to come online in China over the next five years. Below is the summary of upcoming stream cracker projects globally.
Chinese projects that are currently under construction include Wanhua Chemial, Yulongdao Refining & Petrochemical, Sinopec, Jilin Petrochemical and more. Joint venture steam cracker projects in China between domestic producers and multinational corporations have also started construction which includes Sabic-Fujian Petrochemical, Ineos Sinopec Tianjin, Shell CNOOC Petrochemical, BASF Zhanjiang, and ExxonMobil. These projects will increase ethylene capacity by 21.8mn t over the upcoming five years. Asian nations excluding China includes S-oil South Korea, Hindustan Petroleum India, Lotte Chemical Indonesia have also started construction which totals 5.2mn t of ethylene capacity.
Borouge, SATORP and a joint venture between CP Chem and Qatar Energy in the Middle East are also investing in new crackers with a total capacity addition of 5.2mn t. In Europe, Ineos Project One and PKN Orlen have announced projects while Sabic UK invested in a green project. The Sabic project involves restarting and converting its current cracker to run on hydrogen.
Russia has steam cracker projects slated to start up in the five-year span, including Nizhnekamskneftekhim, Irkutsk Oil, Baltic Chemical, and Amur GCC while Uzbekistan has also announced an expansion from Gas Chemical Complex. North America has three projects slated to come on over the next five years that will increase its capacity by 3.6mn t. North American projects include Shintech US, Joint venture CP Chem Qatar Energy, and Dow in Canada.
Argus’s Ethylene Analytics includes a global plant-level capacity dataset detailing expected project timelines.
Author: Dhanish Kalayarasu
Date: 15/05/2024
Spotlight content
Related news
Hormuz naval escort unlikely in the near-term: SSY
Hormuz naval escort unlikely in the near-term: SSY
London, 4 March (Argus) — A US plan for its navy to escort ships heading through the strait of Hormuz is unlikely to come to fruition any time soon because the fleet will be occupied with military operations, according to analysts at shipbroker SSY. Traffic through the strait, the world's most critical oil and LNG shipping lane at the mouth of the Mideast Gulf, has almost entirely stopped, with insurers unwilling to cover transit since Iran said it will "burn" any ship that tries to pass. A container ship was struck today in the strait, UKMTO said. US president Donald Trump stated on 3 March that "if necessary, the United States Navy will begin escorting tankers through the strait of Hormuz, as soon as possible." Europe is also looking at naval operations in the region, with French president Emmanuel Macron announcing on Tuesday the creation of a coalition to secure traffic through Hormuz. But SSY said the US Navy "has privately told the industry it will lack escort capacity until the initial stage of the military operation is complete. An additional issue is that US law does not allow the country's navy to escort ships that are not US-flagged or -owned, or have no US crew, the firm said. In addition to the legal issues, SSY pointed to the difficulty of actually protecting shipping in the strait. "Physical geography favours the attacker," it said. "[Shipping] lanes are 2 [nautical miles] wide each direction; vessels transit at 10–12 knots and must turn at the narrowest point adjacent to Iranian islands. "A destroyer can intercept missiles but cannot simultaneously sweep mines, counter drone-boat swarms from multiple bearings, and manage GPS disruption," SSY said. The firm pointed to recent US operations in the Red Sea at the height of attacks by Yemen-based Houthi militants, where "escorts failed to restore commercial traffic despite ~400 drones/missiles downed". But, SSY said, pressure to restore normality is greater this time, which could lead to a significantly different military strategy. By John Ollett and Andrey Telegin Send comments and request more information at feedback@argusmedia.com Copyright © 2026. Argus Media group . All rights reserved.
Mideast war to tighten LatAm polymer supply: Update
Mideast war to tighten LatAm polymer supply: Update
Add information on shipping at Strait of Hormuz, Red Sea and Mideast Gulf regions. Sao Paulo, 3 March (Argus) — The US-Iran war has heightened security risks across Middle East sea lanes and disrupted polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP) flows into Brazil and the wider Latin American market as carriers suspend loadings, impose emergency surcharges and reroute vessels around the Cape of Good Hope. Some containership owners, such as CMA CGM, earlier announced an "emergency conflict surcharge" of $3,000/feu (forty-foot container), or $121/metric tonne (t), on all loadings from ports in the Mideast Gulf and Red Sea regions but have since suspended operations out of the Mideast Gulf. Shipping is now possible only from the Red Sea region and some ports outside of the Mideast Gulf, but the situation remains dynamic and it is unclear which carriers are still calling at these ports, particularly when sailings involve transiting through the Bab el Mandeb strait. Despite the cost surge, vessel space remains constrained as shipowners cut departures on high-exposure routes and roll bookings. Capacity tightness is most visible on short-notice shipments to South America's east coast, a global trader said. Rerouting vessels around the Cape of Good Hope is lengthening voyages and creating equipment imbalances, stretching lead times and undermining production planning for converters dependent on imported resin. Buyers report more blank sailings, delayed laycans and shifting arrival times as carriers adjust rotations. Additional insurance requirements and onboard security measures are adding time and cost, weakening schedule reliability into Santos, Manaus and other Brazilian ports. Transit through key canals is technically "restricted and unreliable" rather than fully closed, but the operational outcome is similar, with fewer departures from Gulf export hubs and fewer relay options into Mediterranean transshipment points, a source said. Equipment shortages on feeder services and rising premiums for guaranteed space are adding further friction. Higher landed polymer costs The conflict's immediate effect on Latin American polymer markets is rising landed costs. Import-parity formulas are absorbing new surcharges and longer routes, lifting cfr Brazil indications even without adjustments to fob values. If reduced departure frequency persists, participants expect spot tightness to surface into late March, particularly for PP grades with limited substitution options on the demand side. Domestic production can offset part of the shortfall but cannot fully cover a sharp reduction in Middle Eastern arrivals if carriers deepen schedule cuts. Middle Eastern suppliers remain central to Brazil's polymer balance. Saudi Arabia was Brazil's second-largest PP supplier in 2025, sending almost 140,080t, or 20pc of the country's imports. As for PE, Saudi Arabia ranked third at 56,445t, while Egypt placed fifth with nearly 47,795t last year. Brazilian polyvinyl chloride (PVC) buyers also increased purchases from Egypt by 68pc last year to around 100,090t. Converters are adjusting sourcing strategies by front-loading purchases, widening delivery windows and considering alternative origins with lower exposure to higher-risk routes, even when nominal resin prices are higher. "The situation will not normalize in one or two weeks," one source said. "News changes by the hour, owners are cautious, and freight alone will lift cfrs across Brazil and the rest of Latin America." Market participants describe the disruption as global. With elevated risk premiums and major carriers avoiding vulnerable passages, surcharges and extended transits are expected to persist, supporting delivered PE and PP values until security conditions allow a broader return to standard routes. Aiming to restore normal transits, president Donald Trump on Tuesday said the US will offer political risk insurance and naval convoys for ships transporting energy and other commodities through the Mideast Gulf. Meanwhile, Brazil petrochemicals giant Braskem has also adjusted its domestic pricing in response to the tighter logistics environment. The company withdrew the pricing policy it released on 28 February and issued a revised schedule on 2 March, increasing PE and PP prices across all grades. Braskem lifted LDPE, HDPE, LLDPE and metallocene PE values by R500/t ($95/t), with no bonuses applied. As for PP, the company raised homopolymer and copolymer prices by R250/t, also without bonuses. Market participants said the revision reflects both escalating freight costs and expectations of reduced availability from traditional import origins. Brazil's naphtha cost could rise The US–Iran conflict is adding pressure to Brazil's chemical chain through higher oil prices, exchange rate volatility and tighter availability of key feedstocks, chemical industry association Abiquim said on 3 March. While no physical disruptions have emerged, Abiquim warns that a sustained increase in Brent crude values will raise petrochemical naphtha costs, a structural vulnerability for a country that remains a net importer of derivatives. Rising energy benchmarks could narrow petrochemical margins and weaken Brazil's position against regions that produce more gas. Additional risks extend to nitrogen fertilizers and chemical intermediates, given Iran's role as an exporter of urea, ammonia, methanol and derivatives. Brazil imports about 85pc of its fertilizer needs, leaving agriculture and downstream producers exposed to potential price spikes. Abiquim also cited macroeconomic risks, with geopolitical uncertainty typically driving a stronger US dollar and raising import costs for industrial inputs and equipment. The situation underscores structural weaknesses in Brazil's chemical chain and the need for long-term policies that reduce dependence on imported naphtha, fertilizers and other strategic inputs, the group added. By Fred Fernandes and Isabela Mendes Send comments and request more information at feedback@argusmedia.com Copyright © 2026. Argus Media group . All rights reserved.
Caustic soda freight costs rise on Mideast Gulf war
Caustic soda freight costs rise on Mideast Gulf war
Houston, 3 March (Argus) — Freight costs for US caustic soda exports soared early this week as ship traffic through the strait of Hormuz is at a standstill after the US and Israel attacked Iran on 28 February, redrawing trade routes to key destinations and fueling higher energy costs. Caustic soda freight costs jumped by as much as 50pc from the US Gulf coast compared with last week, various suppliers said. Freight to Brazil topped as much as $180/dry metric tonne (dmt) on Tuesday, marking a 28-38pc increase from late-February estimates, sources said. Additionally, freight costs for transatlantic routes climbed by 37pc, a trader added. Escalating war in the Middle East does not threaten US caustic soda supply availability, nor does it immediately threaten global trade , but lends further support to rising spot values through logistical costs as global suppliers and shippers avoid the strait of Hormuz . Iran on Monday claimed it has "closed" the strait of Hormuz connecting the Mideast Gulf and Gulf of Oman and intends to burn any ship that tries to pass through. Vessel traffic through the key passage for crude, petrochemicals, fertilizers and other commodities has come to a virtual halt in the days after the US and Israel attacked. Higher freight costs from the US further increase net forwards to the Mediterranean and Brazil, but spot export availability from the US is expected to shrink in the next 30-45 days as producers undertake planned turnarounds. Elevated freight combined with seasonal maintenance increased early-week price discussions for new sales, with one source indicating offers could climb into the mid-$400s/dmt fob — a level last seen in June, Argus data show. By Connor Hyde Send comments and request more information at feedback@argusmedia.com Copyright © 2026. Argus Media group . All rights reserved.
Middle East shock to tighten LatAm polymer supply
Middle East shock to tighten LatAm polymer supply
Sao Paulo, 3 March (Argus) — Heightened security risks across Middle East sea lanes because of the US-Iran conflict could disrupt polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP) flows into Latin America as carriers suspend sailings, impose emergency surcharges and reroute vessels around the Cape of Good Hope. Carriers have introduced emergency and war-risk fees on Middle East–Atlantic corridors, market participants said. Traders are citing initial guidance near $1,500/20ft equivalent units and prompt offers around $3,000/40ft container, according to a 2 March Hapag-Lloyd notice seen by Argus . Despite the cost surge, vessel space remains constrained as shipowners cut departures on high-exposure routes and roll bookings. Capacity tightness is most visible on short-notice shipments to South America's east coast, a global trader said. Rerouting away from high-risk zones is lengthening voyages and creating equipment imbalances, stretching lead times and undermining production planning for converters dependent on imported resin. Buyers report more blank sailings, delayed laycans and shifting arrival times as carriers adjust rotations. Additional insurance requirements and onboard security measures are adding time and cost, weakening schedule reliability into Santos, Manaus and other Brazilian ports. Transit through key canals is technically "restricted and unreliable" rather than fully closed, but the operational outcome is similar, with fewer departures from Gulf export hubs and fewer relay options into Mediterranean transshipment points, a source said. Equipment shortages on feeder services and rising premiums for guaranteed space are adding further friction. Impact on Latin America The conflict's immediate effect on Latin American markets is rising landed costs. Import-parity formulas are absorbing new surcharges and longer routes, lifting cfr Brazil indications even without adjustments to fob values. If reduced departure frequency persists, participants expect spot tightness to surface into late March, particularly for PP grades with limited substitution on the demand side. Domestic production can offset part of the shortfall but cannot fully cover a sharp reduction in Middle Eastern arrivals if carriers deepen schedule cuts. Middle Eastern suppliers remain central to Brazil's polymer balance. Saudi Arabia was Brazil's second-largest PP supplier in 2025, sending almost 140,080t, or 20pc of imports. As for PE, Saudi Arabia ranked third at 56,445t, while Egypt placed fifth with nearly 47,795t. Brazilian polyvinyl chloride (PVC) buyers also increased purchases from Egypt by 68pc last year to around 100,090t. Converters are adjusting sourcing strategies by front-loading purchases, widening delivery windows and considering alternative origins with lower exposure to higher-risk routes, even when nominal resin prices are higher. "The situation will not normalize in one or two weeks," one source said. "News changes by the hour, owners are cautious, and freight alone will lift cfrs across Brazil and the rest of Latin America." Market participants describe the disruption as global. With elevated risk premiums and major carriers avoiding vulnerable passages, surcharges and extended transits are expected to persist, supporting delivered PE and PP values until security conditions allow a broader return to standard routes. Meanwhile, Brazil's petrochemicals giant Braskem has also adjusted its domestic pricing in response to the tighter logistics environment. The company withdrew the pricing policy it released on 28 February and issued a revised schedule on 2 March, increasing PE and PP prices across all grades. Braskem lifted LDPE, HDPE, LLDPE and metallocene PE values by R500/metric tonne ($95/t), with no bonuses applied. As for PP, the company raised homopolymer and copolymer prices by R250/t, also without bonuses. Market participants said the revision reflects both escalating freight costs and expectations of reduced availability from traditional import origins. Chemicals The US–Iran conflict is adding pressure to Brazil's chemical chain through higher oil prices, exchange rate volatility and tighter availability of key feedstocks, chemical industry association Abiquim said on 3 March. While no physical disruptions have emerged, Abiquim warns that a sustained Brent increase will raise petrochemical naphtha costs, a structural vulnerability for a country that remains a net importer of derivatives. Rising energy benchmarks could narrow petrochemical margins and weaken Brazil's position against regions that produce more gas. Additional risks extend to nitrogen fertilizers and chemical intermediates, given Iran's role as an exporter of urea, ammonia, methanol and derivatives. Brazil imports about 85pc of its fertilizer needs, leaving agriculture and downstream producers exposed to potential price spikes. Abiquim also cited macroeconomic risks, with geopolitical uncertainty typically driving a stronger US dollar and raising import costs for industrial inputs and equipment. The situation underscores structural weaknesses in Brazil's chemical chain and the need for long-term policies that reduce dependence on imported naphtha, fertilizers and other strategic inputs, the group added. By Fred Fernandes and Isabela Mendes Send comments and request more information at feedback@argusmedia.com Copyright © 2026. Argus Media group . All rights reserved.



