A US-Iran rapprochement could revive 2mn b/d of Iranian exports next year, posing a problem for Opec+ amid a fragile oil market recovery, writes Nader Itayim
A victory for Democratic challenger Joe Biden in next month's US presidential election could seriously complicate the outlook for the Opec+ alliance.
The output reduction agreement between Opec and a group of non-Opec producers has taken unprecedented amounts of crude off the market in response to this year's Covid-induced collapse in oil demand, maintained impressive levels of compliance and largely succeeded in boosting oil prices back above $40/bl. But a Biden presidency would open the door to a possible easing of US sanctions against Iran, a revival of the Iran nuclear deal— known as the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) — and the return to the market of millions of barrels of Iranian crude, at a time when, most forecasters suggest, the world economy will still be grappling with the lingering effects of the pandemic.
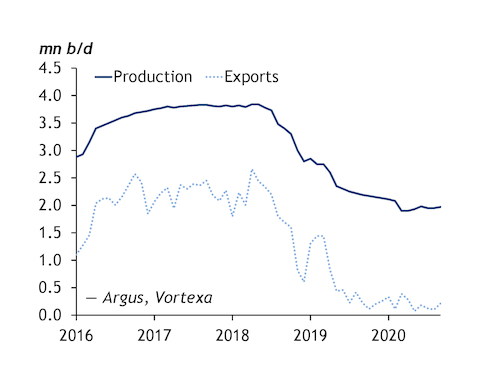
Iran was once Opec's second-largest producer behind just Saudi Arabia, but a devastating cocktail of US, EU and UN sanctions over the past decade has pushed it down to a lowly fifth position, behind Iraq, the UAE and Kuwait. Iran's crude output was 1.96mn b/d in the third quarter, according to Argus estimates, its lowest for more than 30 years (see chart). This is largely because of the sanctions that the administration of President Donald Trump reinstated on the country and its petroleum exports in 2018, following the US' exit from the Iran nuclear deal.
Those and several rounds of new, crushing sanctions targeting Iran's critical financial and banking systems have caused serious damage to the country's economy and contributed to the collapse in value of the Iranian rial. The dollar sold for as much as 322,000 rials on the unofficial market this week, almost nine times what it sold for in January 2017, before Trump took office. President Hassan Rohani says Iran has lost more than $150bn in revenue since the US withdrew from the JCPOA and reimposed sanctions.
But a Biden victory on 3 November could ease some of the short-term pressure on Iran, at least in theory. Throughout his campaign, the former vice-president has made clear his intention to return the US to the JCPOA as part of his plan to re-engage diplomatically with Tehran, arguing that Trump's "maximum pressure" strategy has been "a dangerous failure".
You scratch my back…
As a quid pro quo for change, Biden says Iran will also need to return to "strict compliance" with the nuclear agreement. Tehran began gradually rolling back compliance with its JCPOA commitments in May last year, in response to what it regarded as inaction from the remaining parties to the deal to protect its interests in the face of US sanctions. Iran's position is somewhat similar to Biden's, in that it too has said it will return on the condition that Washington goes back to its commitments, while also compensating Iran for its losses.
On the surface, the solution appears straightforward — resume Washington's participation in the agreement, prompting Iran to do the same. But the reality is likely to be considerably more complicated. "Much of this is about sequencing," says Sanam Vakil, deputy director of the Middle East and North Africa Programme at London-based think-tank Chatham House. "Removing all of the sanctions will be difficult. So, what we are likely to see is a gradual move towards some kind of an interim agreement whereby there is some sanctions relief in return for a rollback of some of the [uranium] enrichment work Iran has carried out since May last year."
Such a "freeze-for-freeze" agreement could lay the groundwork for talks over the kind of broader deal that Biden has said he is targeting. "They will look to sequence sanctions relief and make it contingent on both Iranian compliance and behaviour," Vakil says. "This should keep them in the process."
Another complication is a lack of time. Rohani negotiated the JCPOA in 2015 and would support its revival, but presidential elections next June will end his time in office, as he has already served two consecutive terms. His successor, widely expected to be considerably more conservative, may prove a more challenging adversary. "They will want to get most of this done while Rohani is still in power," Vakil says. "But there are so many things on Biden's to-do list — tackling domestic issues, Russia, China, and repairing the relationship with Europe. I think it might take longer than most imagine."
Should it materialise, an interim agreement would almost certainly involve some kind of relaxation of the embargo that has cut off nearly all of Iran's 2.5mn b/d of pre-sanctions crude exports. The general consensus among many Iran watchers is that this initial agreement could allow for the return of up to 1mn or 1.5mn b/d for a predetermined period, thereby opening the door for talks.
Ready and waiting
Operationally, Iran should have no problem ramping up its exports fairly rapidly, firstly because of the massive amounts of crude and condensate it has built up in onshore and offshore storage, but also because of the care with which state-owned NIOC and its subsidiaries have managed their fields during the sanctions. "Just as they did during the last round of sanctions, they have not shut in the fields — they rotate," says Iman Nasseri, managing director for the Middle East at consultancy FGE. "The fields are kept idle in such a way that they can immediately restart production. They are kept operational and staff levels are maintained, much in the same way that you would take a field off line for a month or two for maintenance."
FGE estimates Iran's crude and condensate inventories at just under 200mn bl, more than half of which is already on the water and could be placed back on the market "overnight", Nasseri says. Iran could realistically ramp its exports back up to 2mn b/d or higher almost immediately, he adds, and move its production back to pre-sanctions levels of nearly 3.8mn b/d within "three, maybe four" months.
While a Biden victory should improve the prospects for a return of Iranian oil to the market, the reality is that, factoring in the time needed for negotiations, these additional barrels are unlikely to materialise until the middle of next year at the earliest, by when cuts under the Opec+ output restraint agreement will have been moderated to 5.7mn b/d, effective 1 January 2021, from the current 7.7mn b/d.
Despite the lag, the return of Iranian exports could spell trouble for an oil market facing renewed warnings over what is increasingly looking like a fragile demand recovery. Following the steady rise in Libyan production in recent weeks, the IEA warns that the expected easing of Opec+ cuts from January means that there is now "limited headroom… to absorb extra supply in the next few months".
This all puts pressure on Saudi Arabia, which has so far adroitly steered the Opec+ response to the Covid demand crisis, but which argues against any drastic change in US policy towards Iran for political as well as oil market reasons. Tensions between Riyadh and Tehran have risen in recent years, culminating in last year's attacks on Saudi oil infrastructure, which Iran is suspected of orchestrating.
Speaking in Washington this week, Saudi foreign minister prince Faisal bin Farhan argued that the current "maximum pressure" campaign is working, even if it has not yet achieved its "final result". But Biden has spoken of the need to "reassess" the US' relationship with the kingdom, and may, if he wins, prove less heedful of Riyadh's concerns than Trump.