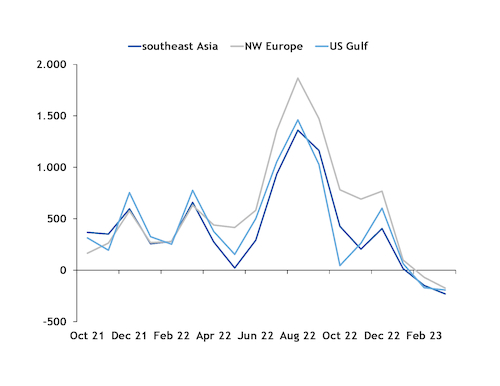
The premium for LNG compared with grey methanol flipped to a discount in February and maintained it through March, a shift that could restore ship owners' interest in LNG for bunkering fuel.
Some ship owners that had been considering LNG for bunkering shifted their sights to methanol last year after LNG prices soared while grey methanol prices did not have as dramatic an upswing. LNG prices in northwest Europe, Asia-Pacific and the US Gulf coast spiked over $2,100/t very low-sulphur fuel oil equivalent (VLSFOe) in August 2022 as uncertainty around Russian winter natural gas exports to Europe intensified. By comparison, grey methanol last year peaked in March at $1,002/t in Asia-Pacific and below $962/t in northwest Europe and the US Gulf coast.
As the 2022/2023 winter season wound down, European natural gas stockpiles remained high. As a result, LNG prices in northwest Europe, Asia-Pacific and the US Gulf coast fell to under $601/t VLSFOe in March, compared with over $720/t VLSFOe for grey methanol in these regions.
Even though LNG and grey methanol are both sourced from fossil feedstock, their CO2 emissions differ. LNG emissions from combustion and full lifecycle are about 21pc and 28pc lower, respectively, compared with emissions from conventional marine fuels. Grey methanol combustion lowers CO2 emissions by only 7pc compared with conventional marine fuels and grey methanol full lifecycle emissions are higher than conventional bunkers. Despite the higher LNG price volatility, LNG provides ship owners with higher CO2 reduction than grey methanol. Methanol also has lower energy content per volume than LNG, and requires fuel tanks approximately 1.3 times larger than equivalent LNG tanks. A vessel owner interested in methanol could opt out of a smaller tank in exchange for shorter voyages.
But, in addition to lower price volatility, methanol has other advantages. It is a liquid fuel at ambient temperatures, which makes it easier to store and handle on board of a vessel compared with LNG, which has to be maintained at least below -177°F to remain liquid. As a result, methanol's operational costs are lower. Methanol is also biodegradable if spilled into water, while an LNG leak could be flammable and explosive. A newbuild vessel with LNG-burning engine costs about 22pc more to build than conventional marine fuel-burning vessel, while an methanol-burning vessel costs about 10pc more to build. Building a methanol bunkering terminal is cheaper than an LNG terminal.
The typical life of a dry bulk carrier, tanker or container ship is about 25 years. A vessel built this year, would end its service by about 2048. When commissioning a vessel with over 5,000 gross tonnage, ship owners travelling the EU territorial waters should consider a requirement considered by the EU to decrease the greenhouse gas intensity of marine fuels by at least 2pc from 2025, 6pc from 2030, 14.5pc from 2035, 31pc from 2040, 62pc as of 2045, and 80pc by 2050, from a 2020 baseline. The EU also agreed to include maritime shipping in its emissions trading system (ETS). Ships will have to pay for 40pc of their emissions from 2024, 70pc from 2025, and 100pc from 2026.
Bio-LNG is fully interchangeable with LNG derived from fossil feedstock. Similarly, bio-methanol is fully interchangeable with grey methanol. Bio-LNG and bio-methanol could be carbon natural, if produced from sustainable biomass. Ship owners who opt to build LNG-burning vessels could burn a blend of bio-LNG with LNG to meet EU's fuel intensity rule and keep their ETS costs down. Ship owners who opt for methanol-burning vessels could burn a blend of bio-methanol with grey methanol. Global production of both bio-LNG and bio-methanol requires scaling up to meet marine fuel demand. Ship owners who choose methanol would have lower vessel building and operational costs. This is countered by the LNG-grey methanol price discount, when LNG-burning vessels owners would see immediate CO2 emissions reductions at lower price.
To hedge their bio-fuel costs and ensure availabilities, ship owners are inquiring about long-term bio-LNG or bio-methanol offtake agreements, looking into partnering with fuel suppliers, or offering their customers more expensive low-carbon freight rates. For example, Danish ship owner Maersk had entered in eight green methanol production partnerships and by 2025 it plans to source over 730,000t of green methanol.